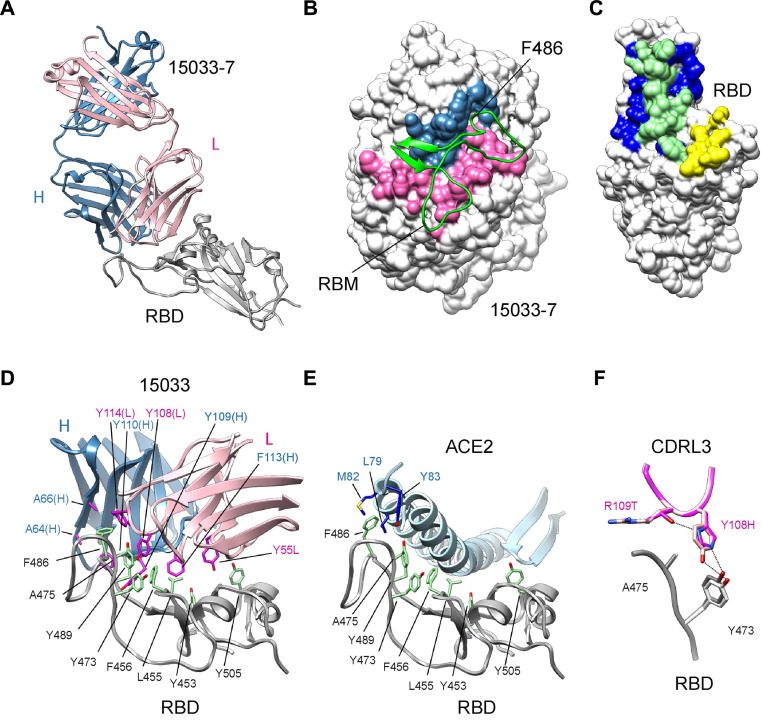
Figure 2.
X-ray crystallographic analysis of Fab 15033-7 in complex with the RBD. (A) Ribbon diagram Fab 15033-7 in complex with the RBD. The RBD is shown in white and the light and heavy chains of the Fab are shown in pink and blue, respectively. (B) Fab 15033-7 (surface representation) and its interaction with the receptor binding motif (residues Leu452 to Ser494, green ribbons) of the RBD. The paratope defined by the Fab-RBD complex is colored blue (heavy chain) and pink (light chain) and the remainder of the Fab is colored white. (C) Surface representation of the RBD colored to show the Fab footprint (blue and green), the ACE2 footprint (yellow and green) and their significant overlap (green). (D) Non-polar residues (magenta) on Fab 15033 (light chain, pink; heavy chain, blue) make key interactions with a stretch of exposed non-polar residues (green) on the RBD (white). (E) The same non-polar residues (green) on the RBD (white) are critical for binding to ACE2 (light blue). RBD residue Phe486 makes key interactions in both the Fab and ACE2 complexes. (F) Fabs 15033 (light pink) and 15033-7 (dark pink) differ by only two residues, both found in CDR-L3. In 15033-7, His108 forms an additional hydrogen bond with Thr109, an interaction that stabilizes the local conformation of the CDR-L3 loop.