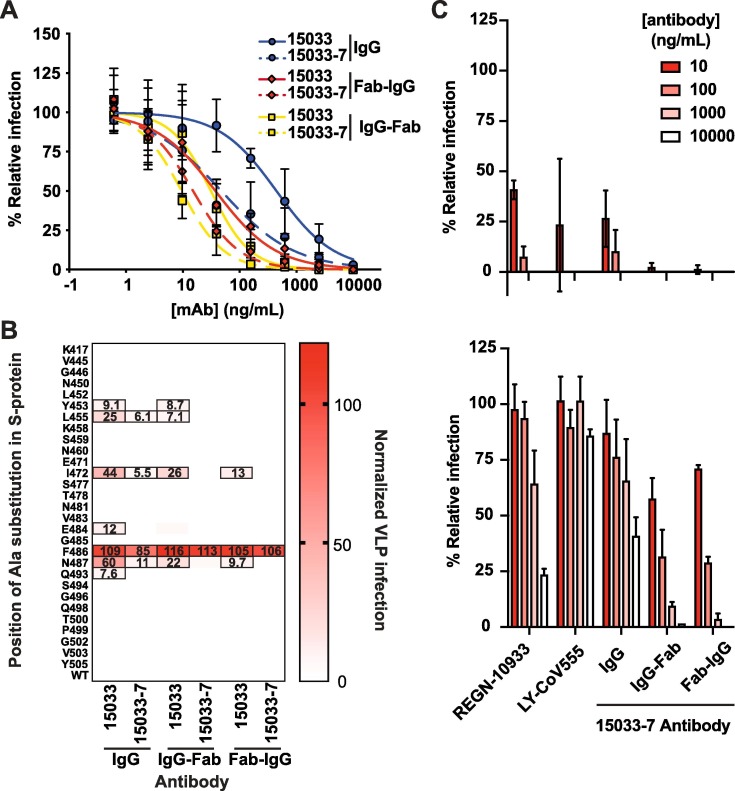
Figure 6.
Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 and pseudotyped VLPs. (A) Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 strain 2019 n-CoV/USA_WA1/2020 by bivalent and tetravalent nAbs (also see Figure S4). The virus was pre-treated with serial dilutions of nAb and infection of ACE2-expressing Vero E6 cells was measured relative to untreated control. Samples were run in triplicate and results are representative of two independent experiments. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. (B) Neutralization of a panel of pseudotyped VLPs displaying SARS-CoV-2 S-proteins with single alanine mutations in or near the ACE2-binding site of the S-protein RBD (also see Figure S5). The VLPs were treated with 50 nM of the indicated nAb and uptake by ACE2-expressing HEK-293 cells was measured in duplicate, and results are representative of two independent experiments. The heat map shows uptake normalized to uptake in the absence of nAb. Boxed cells indicate VLP mutations that represent potential escape vulnerabilities for a given nAb, as defined by > 5% uptake with nAb treatment compared with untreated control (the percent uptake is shown in each cell). (C) Ab-mediated neutralization of isogenic strains of the D614G (upper panel) and B.1.351 (lower panel) SARS-CoV-2 variants, as assessed in the focus reduction neutralization assay at the indicated Ab concentrations relative to assays conducted in the absence of Ab.