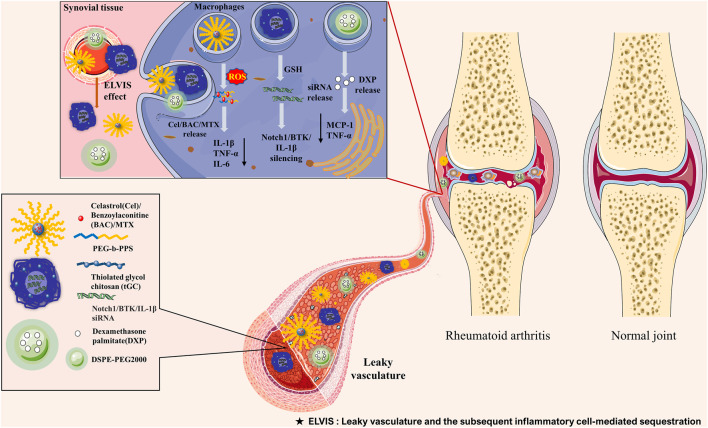
FIGURE 2.
Schematic illustration of the passive targeting delivery system for the management of rheumatoid arthritis by manipulating macrophages with nanocarriers encapsulating various therapeutic agents. Polymer nanoparticles, chitosan nanoparticles, and polymeric micelles have been used for the treatment of RA. Upon intravenous administration, nanoparticles accumulate in the inflamed joints via the ELVIS effect. Subsequently, these nanoparticles are taken up by activated macrophages and selectively deliver Cel, BAC, MTX, DXP, and Notch1/BTK/IL-1β siRNA through pH-responsive, redox-responsive, and ROS-responsive approaches. This process reduces the release of MCP-1, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, thus alleviating the progression of RA. BAC, benzoylaconitine; BTK, Bruton’s tyrosine kinase; Cel, celastrol; DXP, dexamethasone palmitate; ELVIS, Extravasation through Leaky Vasculature and the subsequent Inflammatory cell–mediated Sequestration; GSH, glutathione; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; IL-6, interleukin-6; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; MTX, methotrexate; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; ROS, reactive oxygen species; siRNA, small interfering RNA; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α.