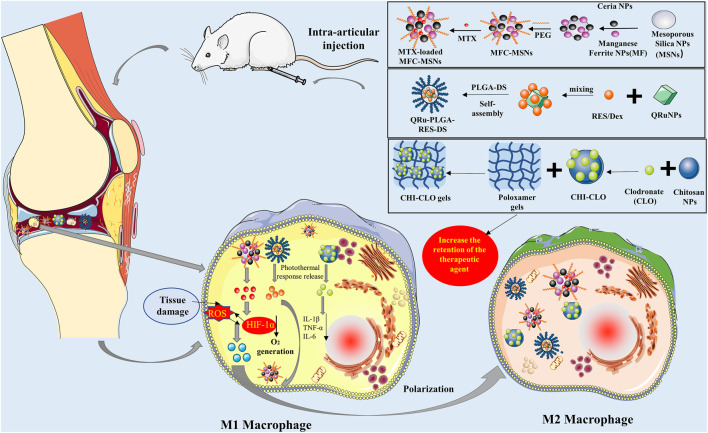
FIGURE 4.
Preparation and application of MTX-loaded MFC-MSN nanoparticles (NPs), QRu-PLGA-RES-DS NPs, CHI-CLO gels, and intra-articular injection of NPs into an RA model mouse. (1) MFC-MSNs synergistically scavenge ROS and produce O2, leading to the polarization of pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages to the anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype in hypoxic and inflamed synovial joints. (2) As photothermal agents, the Ru NPs control the precise release of the RES through the photothermal effect and achieve high-efficiency polarization of M2 type macrophages for treating RA. (3) CHI-CLO NPs were added into the poloxamer gel matrix for intra-articular administration, which increased CLO retention in the joint, improved the therapeutic effect, reduced the side effects, and inhibited the release of IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6 in macrophages. CHI-CLO, chitosan-clodronate; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; IL-6, interleukin-6; MTX, methotrexate; MFC-MSNs, manganese ferrite and ceria nanoparticle–anchored mesoporous silica nanoparticles; PEG, poly (ethylene glycol); QRu-PLGA-RES-DS, quadrilateral ruthenium-poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid)-resveratrol-dextran sulfate; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; ROS, reactive oxygen species; Ru, ruthenium; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α.