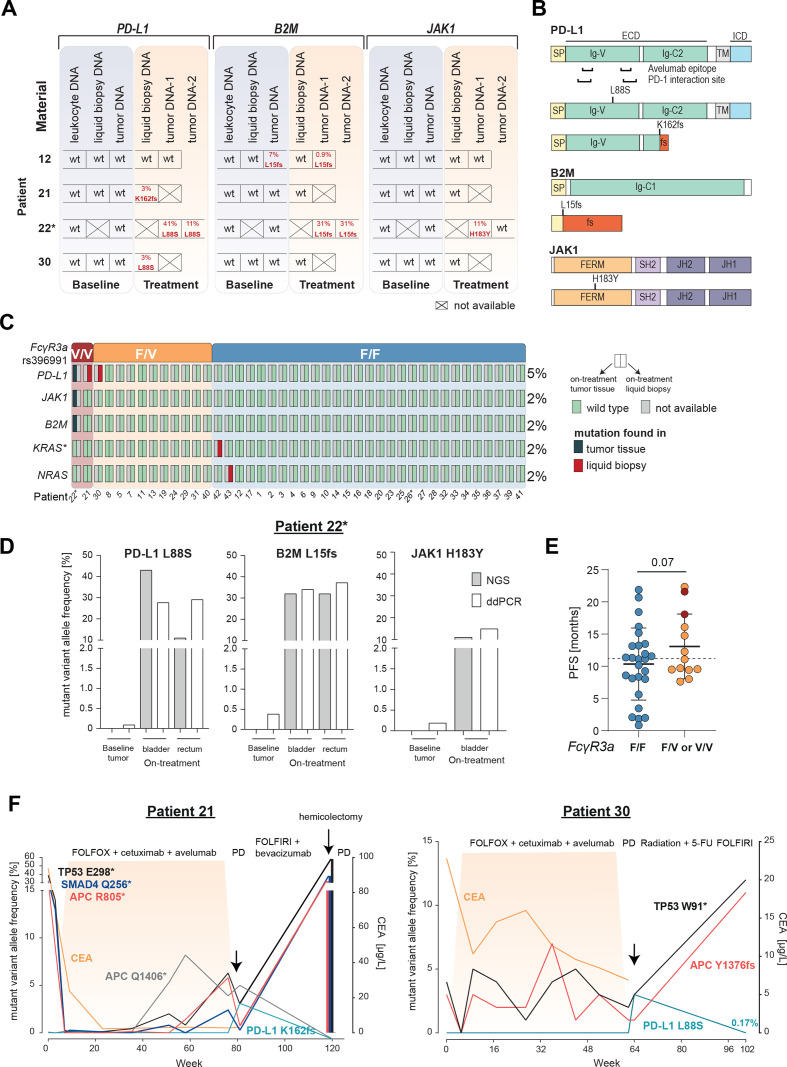
Figure 3.
Selection of resistance variants on AVETUX protocol and clearance after avelumab withdrawal. (A) Overview of B2M, JAK1 and PD-L1 mutations in baseline and on-treatment tumor and liquid biopsy samples. Tumor samples collected under treatment or at EOT originate from: patient 12: liver metastasis, patient 22: tumor DNA 1: rectum and tumor DNA 2: bladder (same metastatic site as used for baseline testing),. (B) Localization of B2M, JAK1 and PD-L1 mutations. (C) Distribution of emerging resistance mutations to avelumab and cetuximab as well as FcγR3a genotype (rs396991) over the cohort. Asterisk on KRAS indicates that mutation disappeared in follow-up liquid biopsy samples. In total five on-treatment tumor samples were available. (D) ddPCR validation of immune checkpoint blockade resistance variants in patient 22. (E) PFS of patients with F/F versus F/V or V/V FcγR3a genotype (rs396991). Dotted line indicates median PFS of entire patient cohort. Statistical test: one-sided, unpaired t-test. (F) Longitudinal ctDNA and biopsy (hemicolectomy) mutational and CEA profile of patient 21 with a treatment-induced PD-L1 K162fs mutation and patient 30 with a treatment-induced PD-L1 L88S mutation. Treatment is indicated above each plot. Highlighted area indicates time during AVETUX regimen. Patients with MSI are marked with asterisk. APC, adenomatous polyposis coli; B2M, β2-microglobulin; CEA, carcinoembryonic antigen; JAK1, Janus kinase 1; PD-L1, programmed cell death ligand 1; PFS, progression-free survival; PD, progressive disease; PR, partial response; TP53, tumor protein p53;