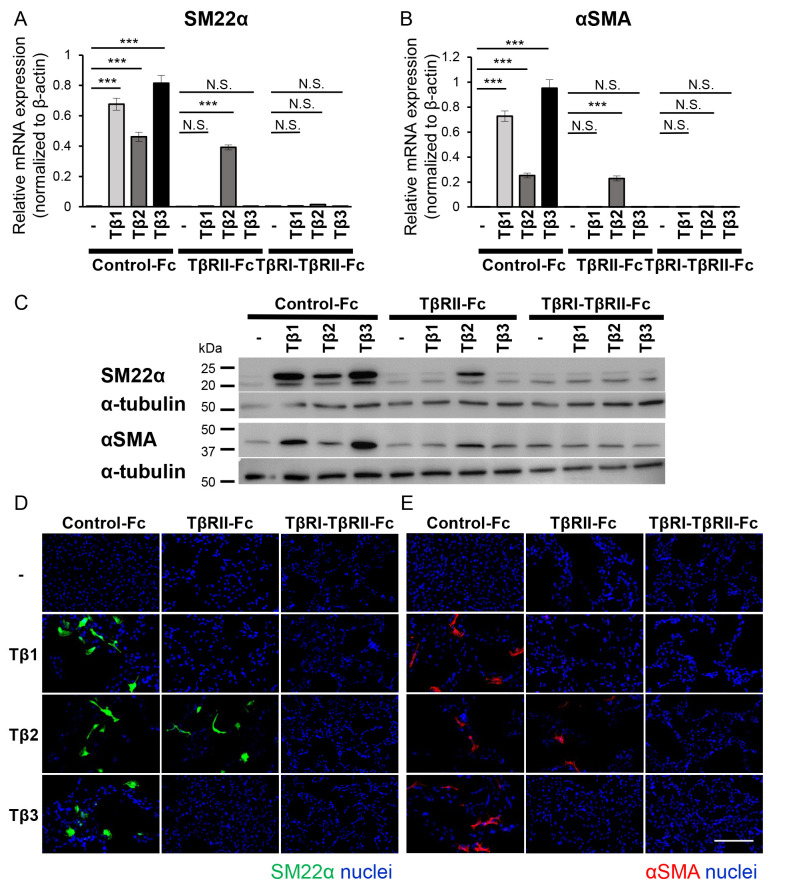
Figure 4.
TβRI-TβRII-Fc chimeric receptor inhibits the TGF-β-induced EMT program in B16 cells. B16 cells were incubated in the absence (−) or presence of TGF-β isoforms [TGF-β1 (Tβ1), TGF-β2 (Tβ2), or TGF-β3 (Tβ3)] (3 ng/ml) in combination with conditioned media from 293T cells containing Fc chimeric receptors (Control-Fc, TβRII-Fc, or TβRI-TβRII-Fc). The activation of the EMT program, was estimated by (A and B) RT-qPCR analyses, (C) immunoblotting and (D and E) immunocytochemistry. Each experiment was performed in triplicate and repeated twice. (A and B) The RT-qPCR analysis for the expression of mesenchymal markers (A) SM22α and (B) αSMA. All data were normalized to the β-actin expression. (C) The immunoblotting analysis of the expression levels of SM22α, αSMA and α-tubulin (loading control). (D and E) Immunofluorescence staining of (D) SM22α (green) and (E) αSMA (red). The nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue). Scale bar, 100 µm. Error bars, SD. ***P<0.001. TβRI, TGF-β type I receptor; TβRII, TGF-β type II receptor; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative PCR; SM22α, smooth muscle protein 22α; αSMA, α-smooth muscle actin; NS, not significant.