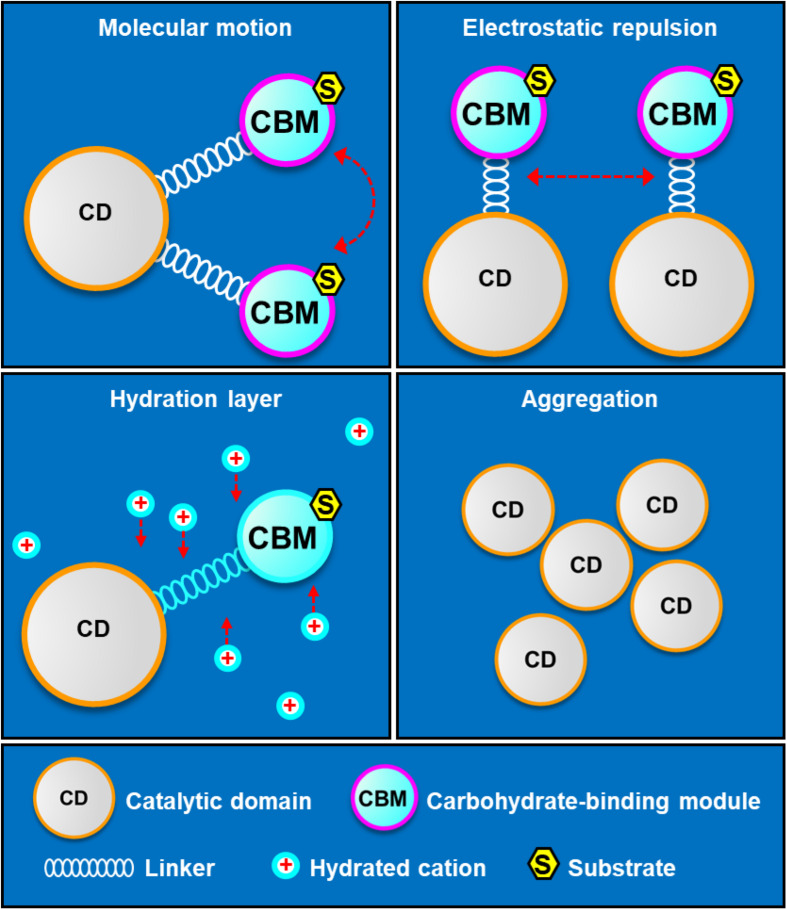
FIGURE 8.
Schematic diagram of structural determinants of cold adaptation and salt tolerance of SdG5A. The highly flexible linker-CBM structure allows an active molecular motion, which guarantees searching and capturing substrates for catalytic domain. The high density of identically charged residues in the linker-CBM region allows appreciable electrostatic repulsion, which prevents protein aggregation and inactivation. The acidic residue-rich linker-CBM structure allows the formation of hydration layer, which help protein maintain in soluble state.