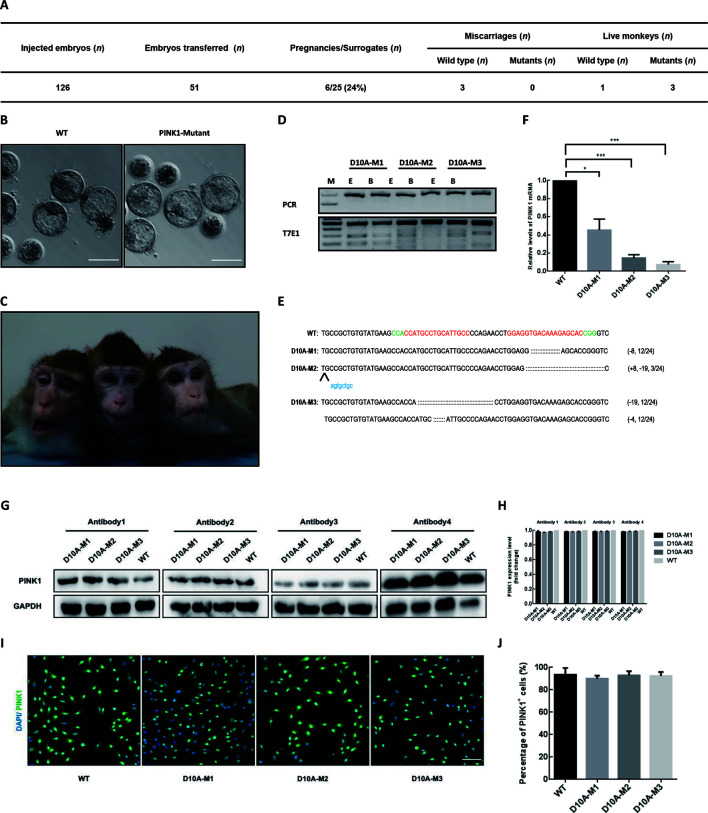
Figure 2.
Paired Cas9-D10A nickases enable one-step generation of PINK1 mutant monkeys
A: Summary of embryos injected, transferred, impregnated, and birthed. B: Representative images of blastocysts developed from zygotes injected with or without Cas9-D10A mRNA and sgRNA. Scale bars: 200 μm. C: Photo of D10A-M1, -M2, and -M3 (left to right) (taken when the monkeys were 3 years old). D: T7E1 cleavage assay of target site containing DNA products amplified from ear or blood tissue of mutant monkeys (D10A-M1, -M2, and -M3). Top panel represents undigested PCR bands and bottom panel represents digested PCR products. E: Ear; B: Blood; M: Marker. E: Editing profiles of mutant monkeys. Regions containing target sites were amplified from mutant fibroblasts and PCR products were subjected to TA cloning. Single TA clones were selected and analyzed by DNA sequencing. For WT allele, PAM sequences are highlighted in green and sgRNA sequences are labeled in red. For alleles with indels, deleted bases are replaced with colons and inserted bases are labelled in lower case and highlighted in blue; deletions (-) and insertions (+). F: RT-qPCR assay on mutant and WT fibroblasts (GAPDH was used for normalization). Compared with WT monkey, all mutant monkeys showed lower PINK1 mRNA expression. ***: P≤0.001; **: P≤0.01; *: P≤0.1. G: Western blotting assay on mutant and WT fibroblasts. H: Relative PINK1 expression levels were calculated using ImageJ 1.8.0 software. Compared with WT monkey, all mutant monkeys exhibited similar PINK1 protein expression. I: Representative images of immunofluorescence staining of mutant and WT fibroblasts. Scale bars: 200 μm. J: Numbers of total cells and PINK1-positive cells were counted using ImageJ 1.8.0 software.