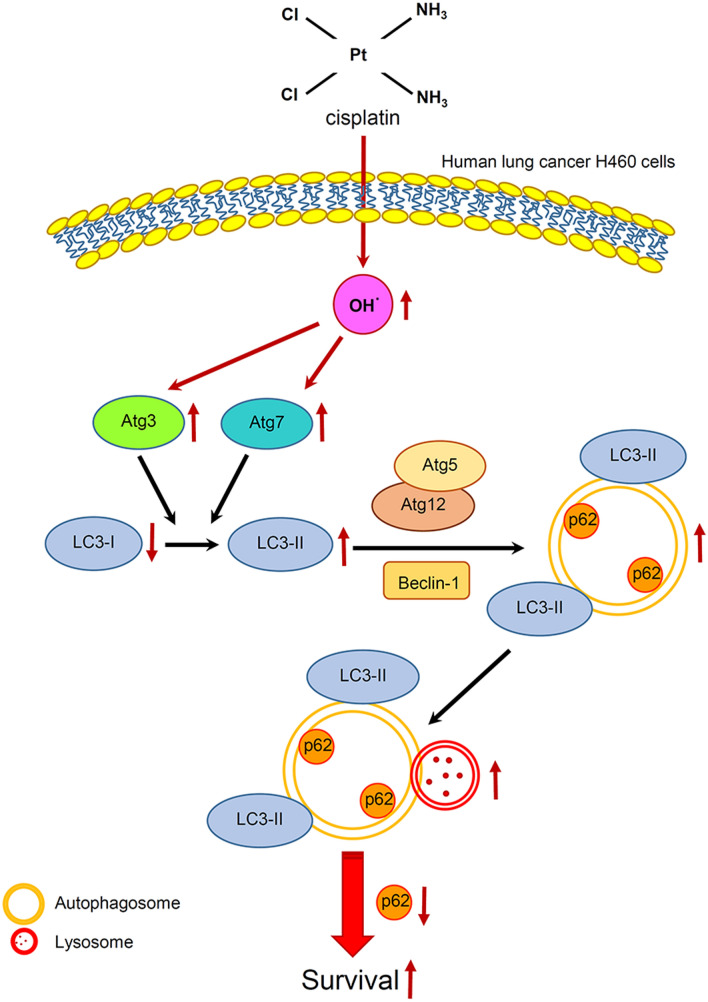
Fig. 8.
Schematic diagram summarizing the proposed mechanism of cisplatin-induced autophagy in human lung cancer H460 cells. Cisplatin elevates cellular hydroxyl radicals (OH·) with consequential activation of Atg3 and Atg7 and conversion of LC3-I to LC3-II. These result in the formation of autophagosomes and reduction of the autophagic substrate p62 through autophagosome-lysosome fusion, and eventually manifest the resistance to cisplatin-induced cell death in human lung cancer H460 cells. Red arrows indicate the modulation on autophagy related molecules induced by cisplatin