Figure 1. Tat-Beclin peptide rescues cardiac I/R Injury in vivo.
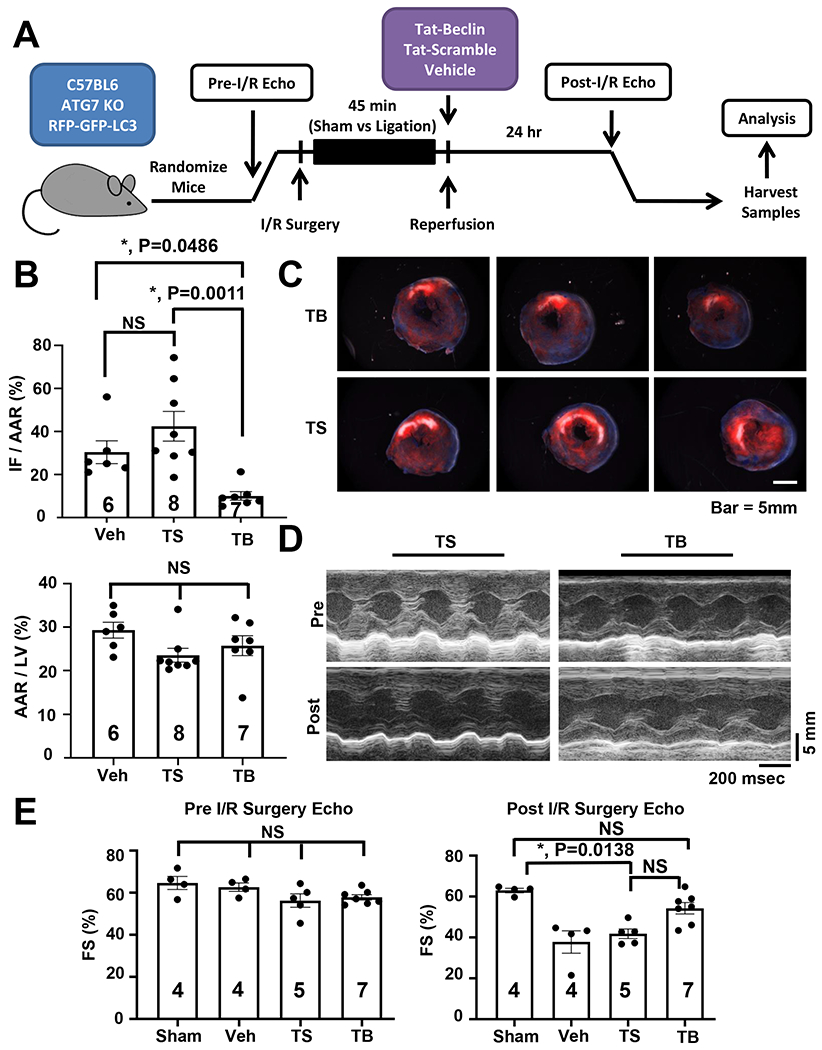
(A) Schematic of in vivo simulated I/R injury model and experimental protocol. (B) Quantification of TTC staining delineating infarct size (IF – infarct, AAR – area at risk, LV – left ventricle) showing reduction of I/R injury with Tat-Beclin administration. N = 6-8, P = 0.0011. (C) Representative cardiac TTC staining histology demonstrating reduction of infarct size with Tat-Beclin treatment. (D) Representative M-mode echocardiogram images. (E) Quantification of cardiac function based on echocardiography (FS – fractional shortening) showing preservation of systolic function in mice receiving Tat-Beclin peptide at reperfusion. Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test was used in all panel. Sham vs. TS, P = 0.001; Sham vs. TB, P = NS; TS vs. TB, P = NS (results of one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test: I/R Veh vs. SAHA, P = 0.0001).
