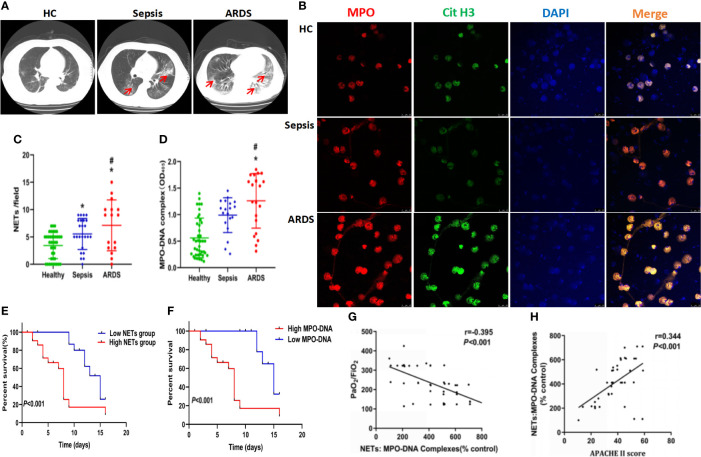
Figure 1.
High levels of neutrophil and neutrophil extracellular traps accumulate in sepsis ARDS patients and correlate with worse outcomes. (A) CT imaging of the lungs of healthy volunteers, sepsis patients, and ARDS patients. (B) Fluorescence imaging of human peripheral blood neutrophils among healthy volunteers, sepsis patients, and ARDS patients for 6 hours. The sections were immunostained with MPO (red) and CitH3 (green), and DAPI (blue) was used to counterstain the nuclei. (C) Ex vivo NET assay of neutrophils in healthy volunteers, sepsis patients, and ARDS patients. (D) Ex vivo MPO-DNA complex ELISA in healthy volunteers, sepsis patients, and ARDS patients. (E) Patient survival curve in the low or high NET group of ARDS patients (n=16). (F) Patient survival curve in the low or high MPO-DNA group. (G) Correlation curve between the MPO-DNA complex and PaO2/FiO2. (H) Correlation curve between APACHE II score and MPO-DNA complex. Statistical analysis was performed using the log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. P < 0.05 (*) and P < 0.05 (#) compared to baseline healthy controls and sepsis patients were considered statistically significant.