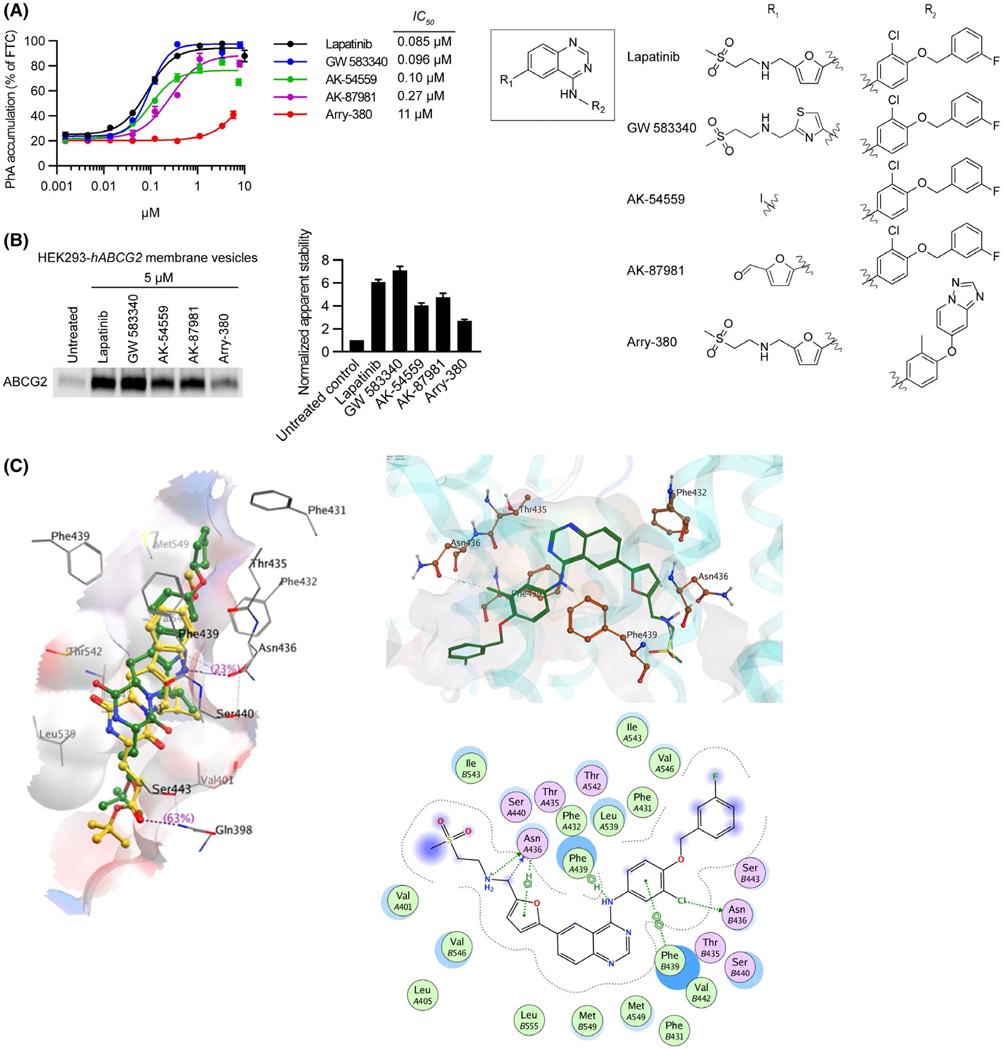
FIGURE 2.
Lapitinib analogs reveal important residues for interacting with ABCG2. A, 0.5 μM of PhA was used as substrate and Fumitremorgin C (FTC) (positive control), Lapatinib, or Lapitinib analogs were used as inhibitors to measure inhibitory effect (IC50) of ABCG2. mAbcg2-KO MEFs expressing human ABCG2 were incubated with PhA and inhibitor for 60 min. Each bar represents the mean ± SE (n = 4). Molecular structures of Lapatinib and its analogs (right). Core structure is shown at the middle, and the individual R1 and R2 constituents of Lapatinib and its analogs GW 583340, AK-54559, AK-87981, and Arry-380 are shown right the core structure. B, HEK293-hABCG2 membrane vesicles were incubated with 5 μM of Lapatinib or Lapatinib analogs for 60 min at 37°C. Samples were heated for 3 min at 62°C. Representative western blot is shown on the left side and the densitometry quantification data from three independent experiments is shown on the right side. C, Diagrammatic representation of Ko143 analog mz29 and lapatinib in the ABCG2 binding cavity. Left panel: the binding of Ko143 (yellow) and mz29 (green) with PDB 6ETI. Right panel: 3D (top side) and 2D (bottom side) representation of Lapatinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, within the ABCG2 binding cavity