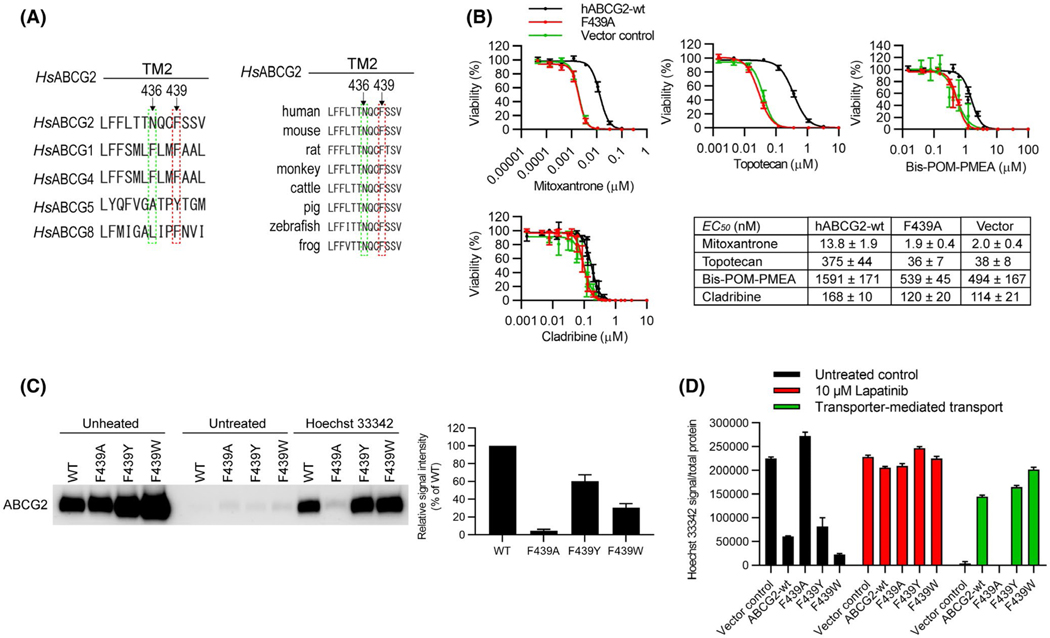
FIGURE 4.
Mutation of the conserved binding residues rescues ABCG2 ligand-binding and transport. A, The human ABCG2 sequence containing the residues N436 and F439 was aligned with the corresponding sequences in its ABCG2 homologs (left) and orthologs (right). The residue F439 in ABCG2 are either conserved or substituted by other hydrophobic residue Y (ABCG5) in the other G-subfamily ABC transporters. The residue N436 in ABCG2 is not conserved in the other G-subfamily ABC transporters (left). The amino acid F439 is conserved in ABCG2 orthologs from frogs to humans (right). B, The cytotoxic effects (EC50 values) were determined by CellTiter-Glo luminescent cell viability assay of cytotoxic drugs Mitoxantrone, Topotecan, Bis-POM-PMEA, and Cladribine using the mAbcg2-KO MEFs expressing human ABCG2-WT (black), ABCG2-F439A (red), or vector control (green). Each bar represents the mean ± SE (n = 5–10). C, MEF-hABCG2-WT, F439A, F439Y, or F439W membrane vesicles were incubated with 10 μM of Hoechst 33342 for 60 min at 37°C. Representative western blot is shown on the left side and the densitometry quantification data from four independent experiments is shown on the right side. D, 0.5 μM of Hoechst 33342 was used as ABCG2 substrate and 10 μM of Lapatinib was used as ABCG2 inhibitor to measure transport activity of ABCG2-WT, F439A, F439Y, and F439W. The cells were incubated with Hoechst 33342 (and Lapatinib) for 120 min. Each bar represents the mean + SE (n = 8)