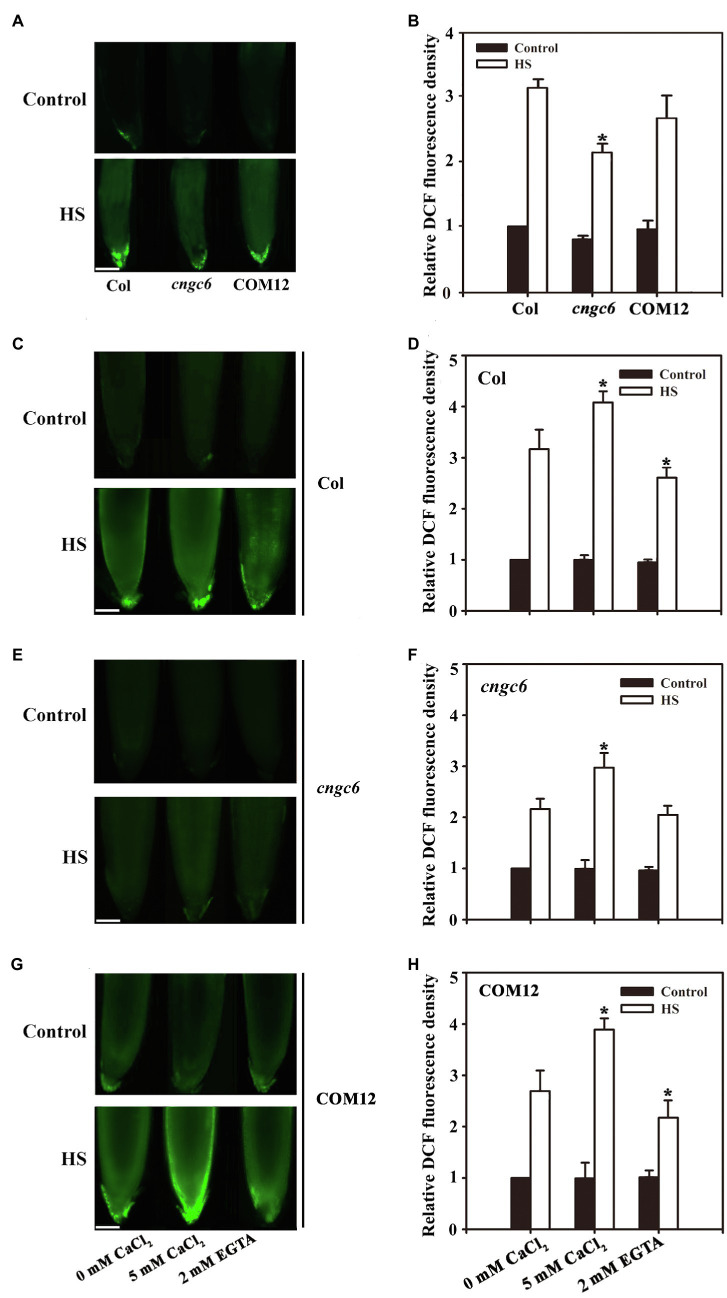
Figure 1.
Effects of calcium ions (Ca2+) on hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) accumulation in Arabidopsis seedlings. (A) About 8-day-old wild-type (WT), cngc6, and COM12 seedlings grown at 22°C were exposed to 45°C (heat shock, HS) or maintained at 22°C (Control) for 30 min. The H2O2 levels in the seedlings were then examined by fluorescence microscopy using roots dyed with 5-(and-6)-chloromethyl-29,79-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (CM-H2DCFDA). Bar = 100 μm. (B) Relative dichlorodihydrofluorescein (DCF) fluorescence densities in the roots. The data presented are the means ± SE of measurements taken from five independent experiments with at least 10 roots for each treatment. *p < 0.05 vs. Col (Student’s t-test). (C,E,G) About 8-day-old seedlings of wild-type (C), cngc6 (E), and COM2 (G) were exposed to 45°C (HS) or maintained at 22°C (Control) for 30 min. The H2O2 levels in the plants were then examined by fluorescence microscopy using roots stained with CM-H2DCFDA. Bar = 100 μm. (D,F,H) The relative DCF fluorescence densities in the roots of wild-type (D), cngc6 (F), and COM2 (H). The data presented are the means ± SE of measurements taken from five independent experiments with at least 10 roots for each treatment. *p < 0.05 vs. 0 mM CaCl2 (Student’s t-test).