Figure 1.
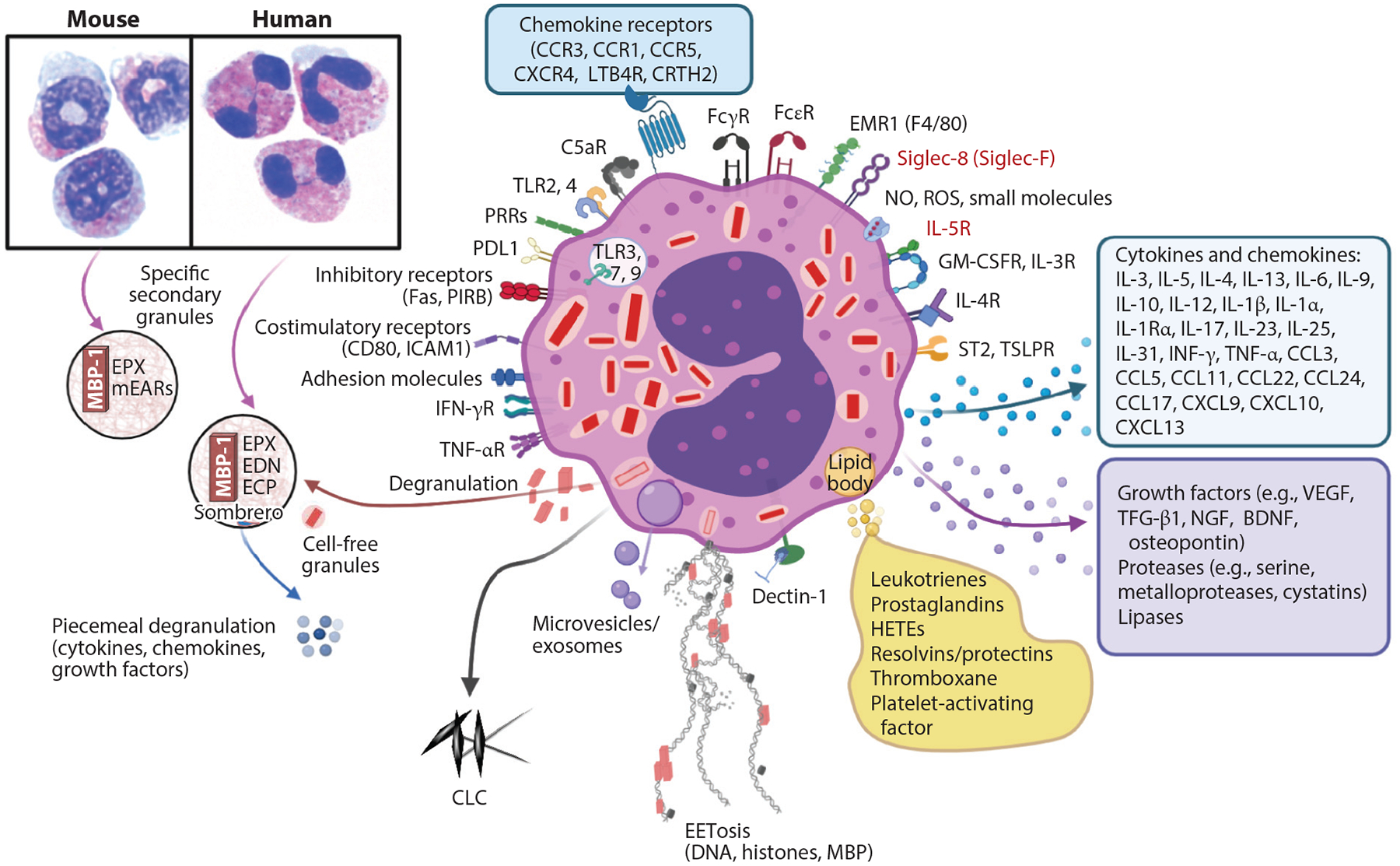
Eosinophil biology. Mouse and human peripheral blood eosinophils show similarities in eosin staining (pink) and differences in nuclei (blue), with mouse nuclei in a circular or figure-eight shape and human nuclei being bilobed, as seen by standard light microscopy. Secondary granules in both contain MBP-1, which creates a crystalline core visible by electron microscopy, and the matrix contains EPX. Human eosinophils have ECP and EDN, whereas mouse eosinophils have only divergent mEARs. Eosinophils undergo several forms of degranulation, including classical exocytosis with release of entire granule contents or piecemeal degranulation, which may occur through formation of sombrero vesicles or exosomes, resulting in the differential release of cytokines, chemokines, or growth factors. Finally, eosinophils may undergo cytolysis, which includes release of cell-free granules and may also involve EETosis whereby DNA, histones, and granule proteins are released, forming extracellular nets. Mediators from lipid bodies are shown, as well as the many cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors. Siglec-8, IL-5R (receptors in red), and IL-5 are targets for monoclonal antibodies to deplete eosinophils. This figure shows some key representative eosinophil molecules and not a complete list. Abbreviations: BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; CCL, C-C motif chemokine ligand; CCR, C-C motif chemokine receptor; CLC, Charcot–Leyden crystal protein; CRTH2, chemoattractant receptor-homologous molecule expressed on Th2 cells; CXCL, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand; CXCR, C-X-C motif chemokine receptor; ECP, eosinophil cationic protein; EDN, eosinophil-derived neurotoxin; EPX, eosinophil peroxidase; FcεR, Fc-epsilon receptor; FcγR, Fc-gamma receptor; GM-CSFR, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor; HETE, hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid; ICAM1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1; LTB4R, leukotriene B4 receptor; MBP-1, major basic protein 1; mEAR, mouse eosinophil-associated ribonuclease; NGF, nerve growth factor; NO, nitric oxide; PIRB, paired immunoglobulin-like receptor B; PDLI, programmed death ligand 1; PRR, pathogen recognition receptor; ROS, reactive oxygen species; Siglec, sialic acid–binding immunoglobulin-like lectin; ST2, suppressor of tumor 2 [also known as IL-1RL1 (interleukin-1 receptor-like 1)]; TGF-β1, transforming growth factor beta 1; TLR, Toll-like receptor; TSLPR, thymic stromal lymphopoietin receptor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor. Figure adapted from images created with BioRender.com.
