Figure 2.
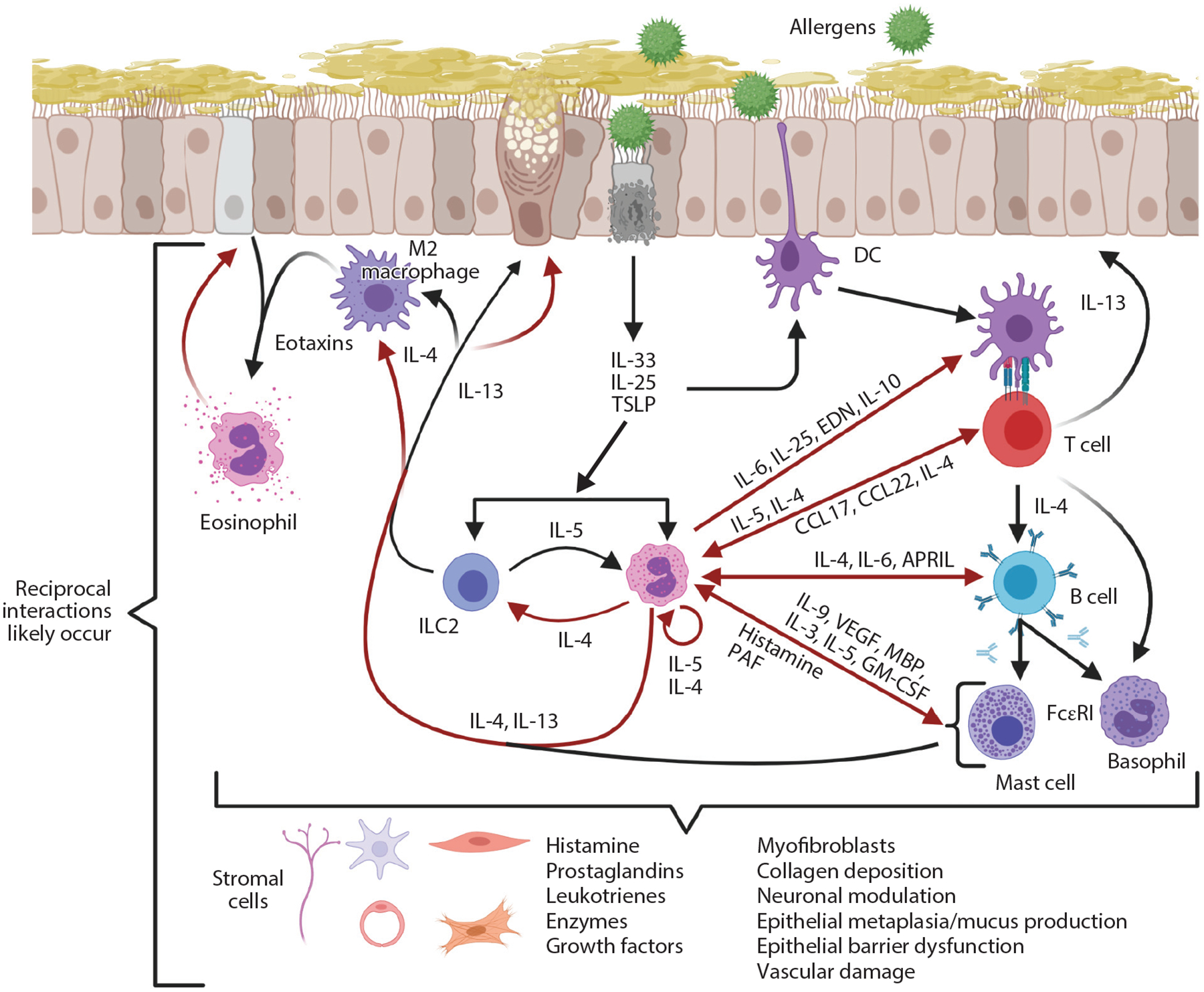
Type 2 immune responses in allergy. Allergens induce epithelial responses that lead to production of IL-33, IL-25, and TSLP, which are immediate cytokine signals released upon epithelial activation or damage. A wide variety of cells, including ILC2s, eosinophils, DCs, eosinophils, M2 macrophages, mast cells, basophils, and Th2 cells, respond to these cytokines. In principle, this can result in reciprocal interactions between these cells to release additional mediators. IL-13 enhances expression of eotaxins to promote eosinophil recruitment and leads to goblet cell metaplasia/mucus production. Red arrows represent products derived from eosinophils. Abbreviations: APRIL, a proliferation-inducing ligand; CCL, C-C motif chemokine ligand; DC, dendritic cell; EDN, eosinophil-derived neurotoxin; FcεRI, Fc-epsilon receptor I; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; ILC2, group 2 innate lymphoid cell; MBP, major basic protein; PAF, platelet-activating factor; TSLP, thymic stromal lymphopoietin; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor. Figure adapted from images created with BioRender.com.
