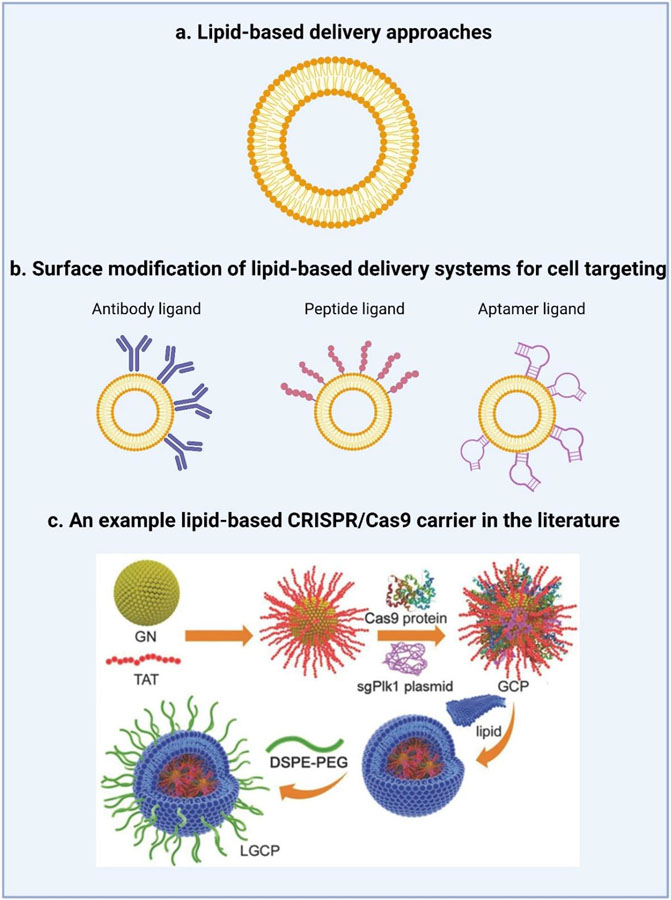
Figure 2. Lipid-based strategies for the delivery of CRISPR/Cas9.
a.) Liposomes are the traditional lipid-based formulations capable of encapsulating both hydrophilic and hydrophobic molecules. b.) To promote cell targeting, the lipid surface can be modified with a ligand, such as an antibody, peptide, or aptamer to interact with the receptors of target cells. c.) From the literature, a schematic diagram of the synthesis of lipid-coated gold nanoclusters (LGCP) adapted from Wang et al.[67] Specifically, the HIV-1-transactivator of transcription (TAT) peptide was used to modify the surface of cationic gold nanoclusters (GNs). The positively charged TAT-GNs and the negatively charged Cas9 proteins and sgRNA plasmids were mixed to form a ternary complex (GCP). GCP was further encapsulated in an anionic lipid shell (1,2-dioleoyl-3-trimethylammoniumpropane (DOTAP)/dioleoyl-phosphatidylethanol-amine (DOPE)/cholesterol, followed by post-modification with polyethylene glycol-phospholipids (DSPE-PEG).[67]