Fig. 1. Long KLC paralogs and isoforms carry an amphipathic helix within their C-terminal domain.
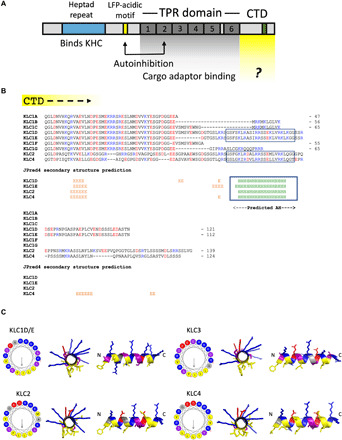
(A) Domain architecture of the KLCs. LFP, leucine-phenylalanine-proline. (B) Manually edited PROMALS3D-based alignment and JPred4 secondary structure predictions for the CTDs of mouse KLC1 to KLC4. Lengths are indicated from a conserved post-KLCTPR QG(L/T)D sequence. H, helix; E, extended. (C) Visualization of the AH in KLC1 to KLC4 using HeliQuest and PyMOL.
