Fig. 3. The AH is required for KLC1ECTD binding to liposomes.
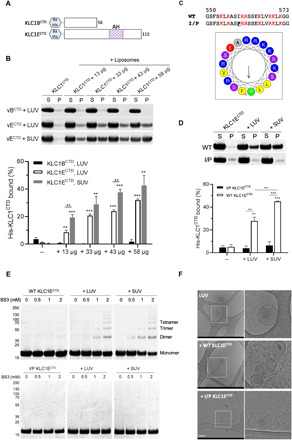
(A) Representation of the His-tagged KLC1B/ECTD constructs. (B) Cosedimentation analysis of His-KLC1B/ECTD with Folch fraction I LUV or SUV. Samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE/Coomassie (top) and quantified by densitometry (bottom). Means ± SEM of at least three experiments. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 compared to the sample without liposomes or as indicated in the graph. (C) Sequence comparison and visualization of the AH in the I560P KLC1ECTD mutant. (D) Cosedimentation analysis of WT or I/P His-KLC1ECTD with Folch fraction I LUV or SUV. Means ± SEM of at least three experiments. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 compared to the sample without liposomes or as indicated in the graph. (E) BS3 cross-linking assay showing oligomers of WT, but not I/P mutant His-KLC1ECTD upon incubation with Folch fraction I LUV or SUV. (F) Cryo–electron microscopy observation of Folch fraction I LUV in the absence or presence of WT or I/P mutant KLC1ECTD. Scale bar, 200 nm.
