FIGURE 2.
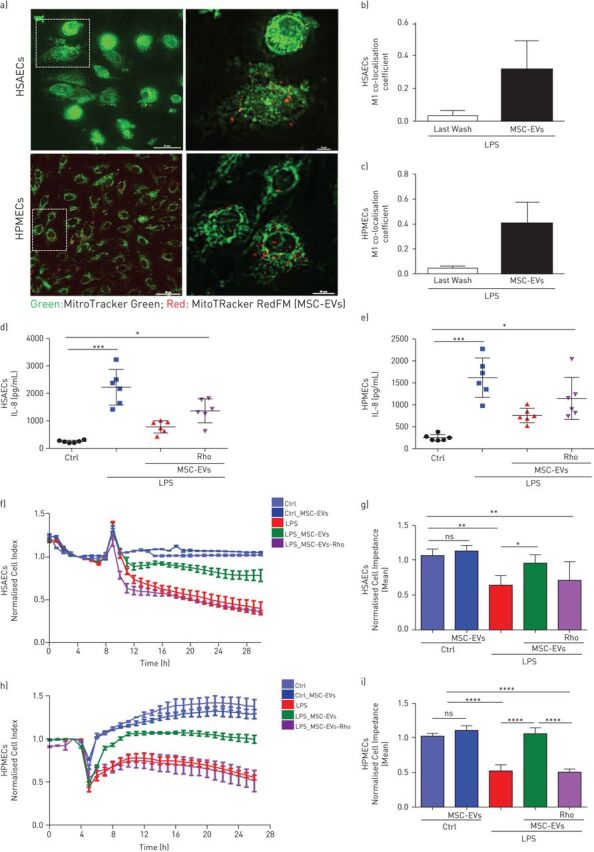
MSC-EVs improve barrier integrity of human primary lung epithelial and endothelial cells through transfer of functional mitochondria. a) Representative live images of MSC-EVs mitochondria internalisation in human small airway epithelial cells (HSAECs) and human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (HPMECs) (Scale bars=50 nm (left panel) and 10 nm (right panel)). b and c) M1 coefficient co-localisation in HSAECs (b) and HPMECs (c). The images were taken using a Nikon 6D Eclipse Ti-E inverted microscope with Okolab touch temperature unit and CO2 environmental chamber (Nikon Instruments, Japan) (40× dry super plan fluor ELWD objective with 0.6 NA). Data are mean±sd of ten images frames. d and e) Levels of interleukin (IL)-8 secretion by HSAECs (d) and HPMECs (e). f) Representative real-time impedance analysis of HSAECs exposed to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and treated with MSC-EVs or MSC-EVs-Rho. g) Cell impedance of HSAECs of XCelligence RTCA measurements. Data are mean±sd (n=3). h) Representative real-time impedance analysis of HPMECs exposed to LPS and treated with MSC-EVs or MSC-EVs-Rho. i) Cell impedance of HPMECs of XCelligence RTCA measurements. Data are mean±sd (n=3). ns: not significant; *: p<0.05; **: p<0.01; ***: p<0.001; ****: p<0.0001. Kruskal-Wallis test with post hoc Dunn's test (d and e). One-way ANOVA analysis with post hoc Bonferroni's test (g and i).
