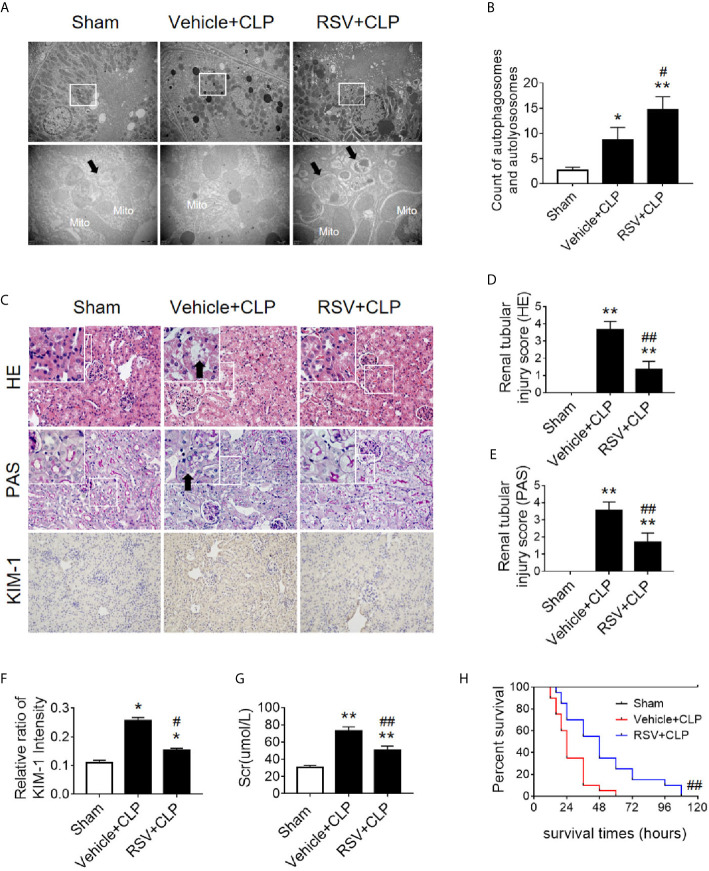
Figure 9.
Activation of the deacetylase Sirt1 by RSV promotes autophagy and reduces SAKI. (A) Effect of Sirt1 activation by RSV on autophagy in the renal cortex of CLP-induced septic mice. Black thick arrows: autophagosomes or autolysosomes; Mito, mitochondria. Upper panel: magnified ×7,000; lower panel: magnified ×40,000. (B) Semi-quantitative analysis of autophagy. The number of autophagosomes and autolysosomes in renal epithelial cells was calculated in 20 randomly selected fields. (C) Effects of Sirt1 activation by RSV on kidney pathology, as evidenced by HE staining, PAS staining, and KIM-1 immunohistochemistry. Upper Panel: Hematoxylin-Eosin (HE) staining (200×; inset: 400×); Middle panel: periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining (200×; inset: 400×). Black thick arrows: Nucleus of RTECs shed to lumen; Lower panel: KIM-1 immunohistochemistry (200×). (D, E) The tubular damage score was evaluated based on pathological observations from HE and PAS staining. These scores are based on the data obtained from the observation of 5 specimens in each group with 10 randomly selected fields of view from a 200× microscope for each specimen. (F) Relative ratio of kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1). The data were obtained from at least three independent experiments. (G) Effect of Sirt1 activation by RSV on the level of sCr. (H) Effects of Sirt1 activation by RSV on the survival times in CLP-induced septic mice. The survival rates were estimated by the Kaplan-Meier method and compared by the log-rank test. n = 20. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 vs. sham group; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 vs. the vehicle + CLP group. CLP, cecal ligation and puncture; RTEC, renal tubule epithelial cell.