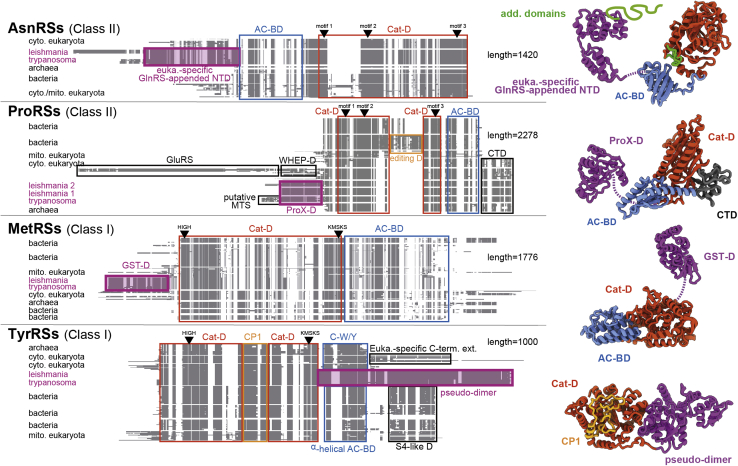
Figure 2.
AsnRS, ProRS, MetRS, and TyrRS harboring additional large functional domains, usually present in other aaRSs. Schematic representation of multiple sequence alignments of aaRS protein sequences, clustered according to the phylogeny. The lengths indicated on the right correspond to the total number of positions for each alignment. Functional domains are boxed and named as follows: AC-BD; Cat-D; WHEP-D; C-W/Y; and S4-like. Catalytic residues (either HIGH and KMSKS or derivatives for class I aaRSs, or motifs 1, 2 and 3 for class II aaRSs) are positioned on the top of each MSA. Additional large known functional domains are boxed and colored in magenta and are GlnRS-appended NTD for the eukaryotic-specific NTD that is appended usually to GlnRS in other eukaryotic species. ProX-D stands for prokaryotic-type editing domain deacylating mischarged Cys-tRNAPro or Ala-tRNAPro, GST-D for glutathione-S-transferase-like domain, and pseudo-dimer for the fused degenerated copy of TyrRS. Cytosolic and mitochondrial ProRSs from L. tarentolae have been corrected/modify according to our RNA-Seq data (see the text and Fig. S5). Homology models of L. tarentolae aaRS sequences are shown on the right of the alignments and serve the purpose of illustrating the positions and sizes of the additional trypanosomatid-specific domains and insertions/extensions. Dashed purple lines represent the link between these large additional domains (their interactions with other domains were not predicted) to other conserved domains of the aaRSs. For the sake of simplicity, all the aaRSs are displayed as monomers. Apart from the GlnRS-appended NTD, the AsnRS includes additional domains that are represented in green thick lines, also highlighted in Figure 3B. aaRSs, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases; AC-BD, anticodon-binding domain; C-W/Y, C-terminal domain homologue to TrpRS; Cat-D, catalytic domain; MSA, multiple sequence alignment; NTD, N-terminal domain; S4-like, small RNA-binding protein S4 domain; WHEP-D, helix–turn–helix domain.