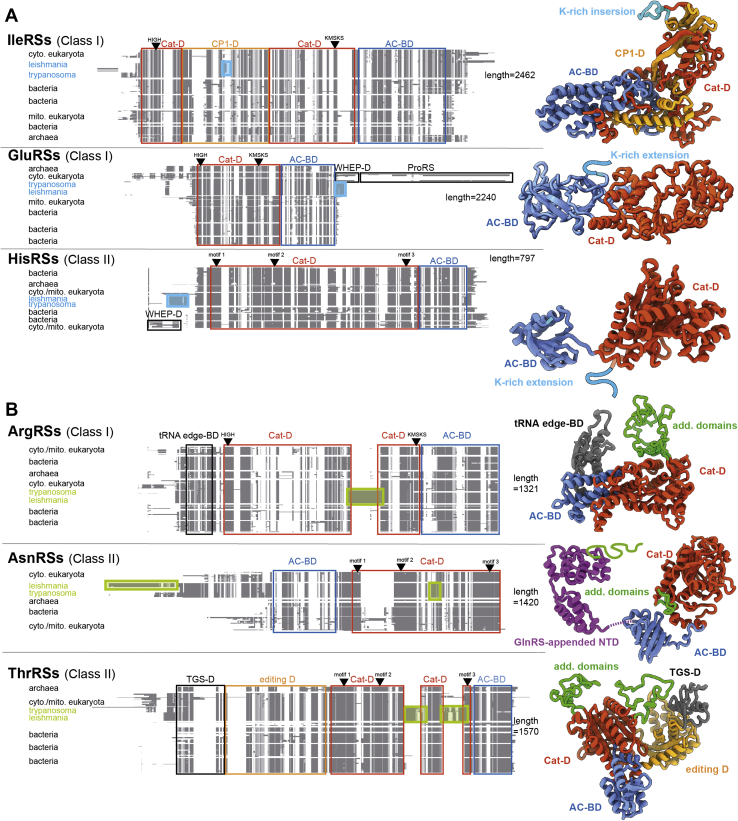
Figure 3.
AaRSs harboring lysine-rich insertion/extension or additional domains of unknown functions.A, IleRS, GluRS, and HisRS harboring a lysine-rich insertion or extension. B, ArgRS, AsnRS, and ThrRS with additional domains of unknown function. Schematic representation of multiple sequence alignments of aaRS protein sequences, clustered according to the phylogeny. The lengths indicated on the right correspond to the total number of positions for each alignment. Functional domains are boxed and named as follows: AC-BD; Cat-D; WHEP-D, and ProRS (which acts as an editing domain). Catalytic residues (either HIGH and KMSKS or derivatives for class I aaRSs, or motifs 1, 2, and 3 for class II aaRSs) are positioned on the top of each MSA. Lysine-rich insertion/extension or additional domains of unknown functions are boxed and colored in blue (A) or green (B), respectively. Homology models of L. tarentolae aaRS sequences are shown on the right of the alignments and serve the purpose of illustrating the positions and sizes of the additional trypanosomatid-specific domains and insertions/extensions. For the sake of simplicity, all the aaRSs are displayed as monomers. Besides the additional domain schematized in green thick lines, AsnRSs from trypanosomatids count an N-terminal GlnRS-appended domain shown in purple, also highlighted in Figure 2. AC-BD; anticodon-binding domain; Cat-D, catalytic domain; CP1, connective polypeptide 1; MSA, multiple sequence alignment; aaRSs, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases; WHEP-D, helix–turn–helix domain found in TrpRS, HisRS, GluRS, and ProRS.