Figure 1. Components of the Ski Complex are required in the germ line for oogenesis.
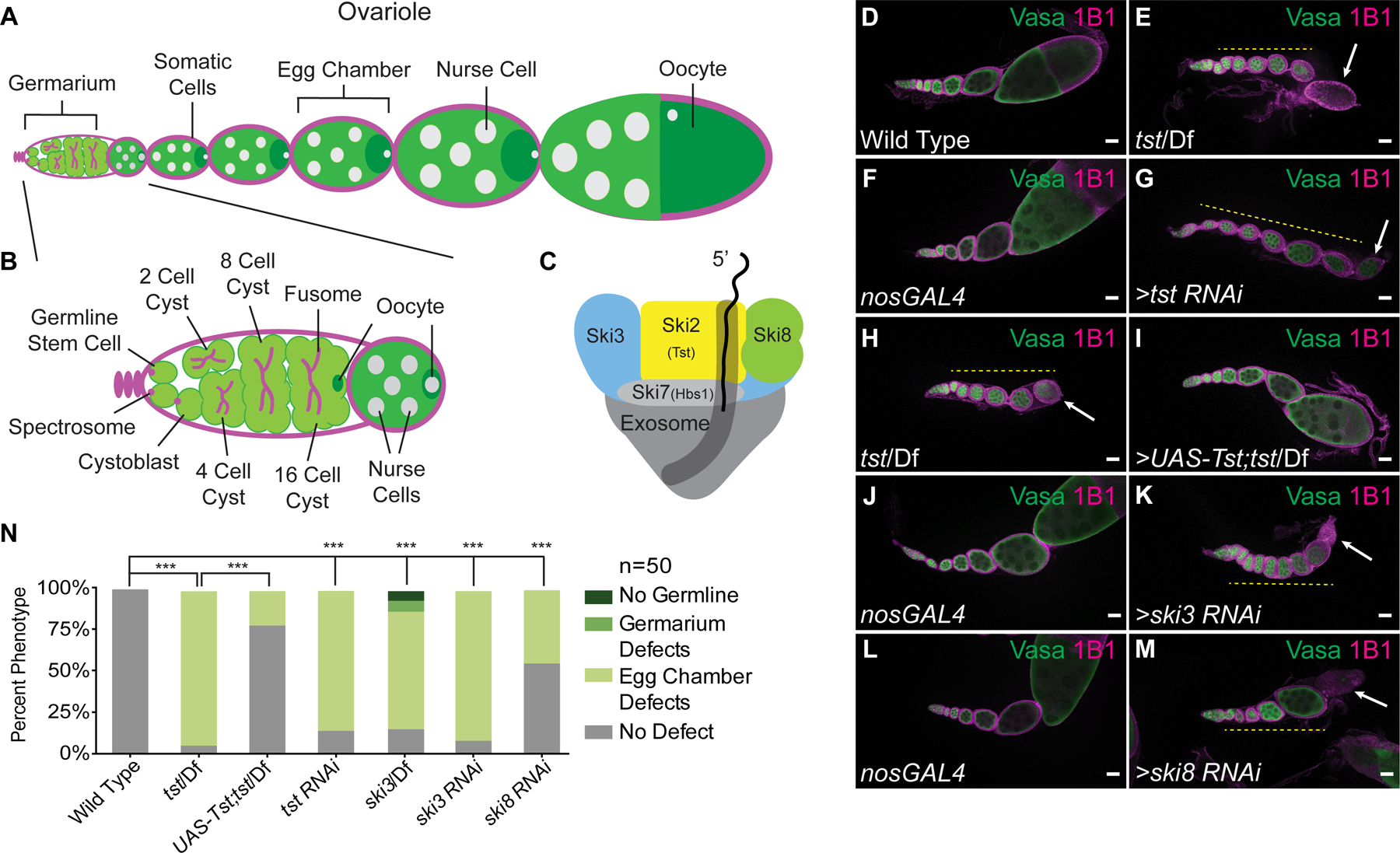
(A) Schematic of a Drosophila ovariole and (B) germarium. (C) The Ski complex is composed of Ski2 (Tst, yellow), Ski3 (blue), Ski8 (green), and Ski7 (Hbs1, light gray) threading mRNA into the exosome (dark gray). (D–M) Confocal images of ovarioles stained with Vasa (green) and 1B1 (magenta). (D) Adult WT ovarioles show normal egg chamber development. (E) Hypomorphic tst genomic mutant ovariole displaying egg chambers that do not grow in size (yellow dashed line) and a dying egg chamber (arrow). (F) nosGAL4 driver control ovariole shows WT morphology. (G) tst germline RNAi knockdown ovariole displaying egg chambers that do not grow in size (yellow dashed line) and a dying egg chamber (arrow). (H) tst genomic mutant ovariole (control for I) showing egg chamber defects (yellow dashed line) and dying egg chamber (white arrow) (I) tst genomic mutant ovariole expressing recombinant Tst protein in the germline rescues the egg chamber defects. (J–M) Germline RNAi knockdown for ski3 (K) and ski8 (M) also display egg chambers that do not grow in size (yellow dashed line) and dying egg chambers (arrow), whereas nosGAL4 driver controls (J, L) have WT egg chambers. (N) Quantification of oogenesis defect phenotypes (n=50 ovarioles per genotype, *** = p < 0.001, Chi-squared tests with Bonferroni correction, df=3). tst/Df and tst RNAi are not significantly different. Scale bars = 10µm. See also Figure S1.
