Figure 1. B cells are in proximity of parenchymal macrophages and they modulate the resident myocardial macrophage pool composition in the naïve heart.
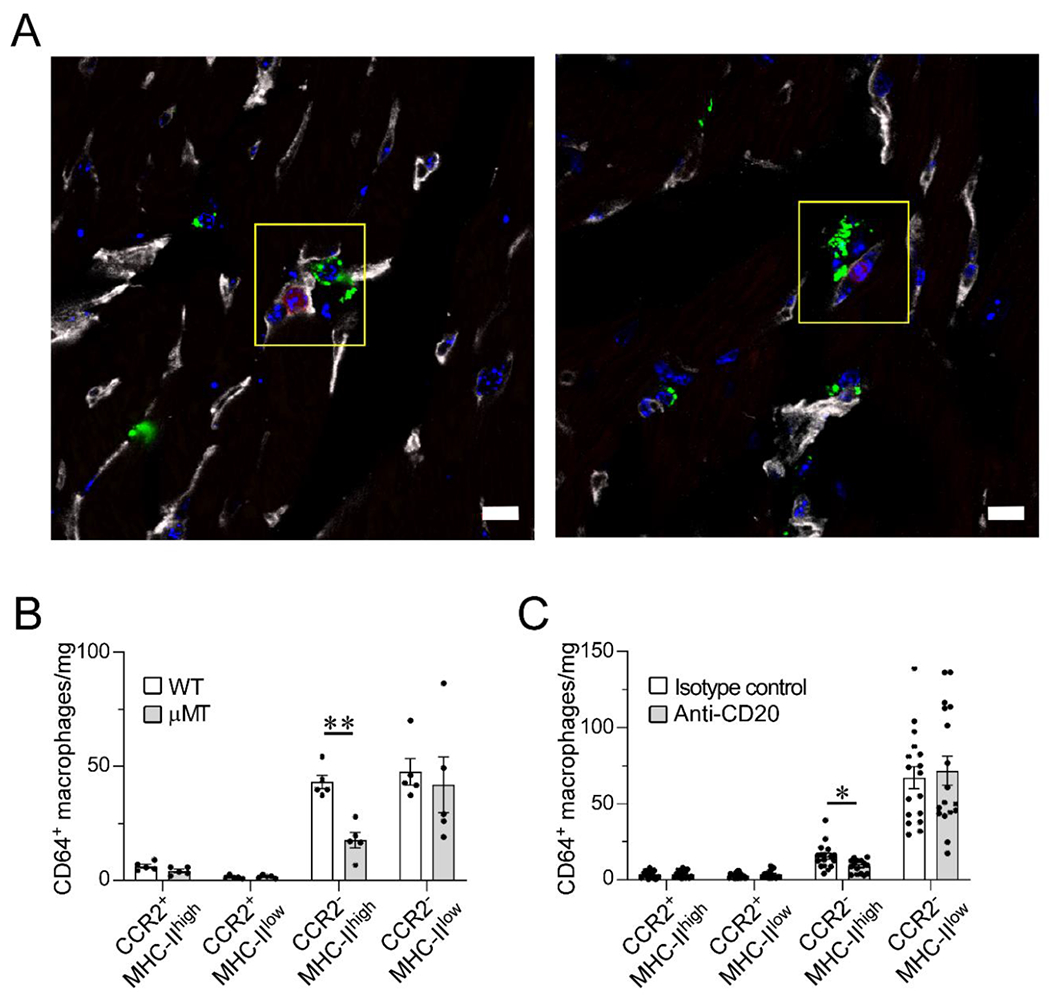
(A) Confocal images of immunostained myocardial sections from a CD19-tdTomato reporter mouse. CD19+ B cells (red) are intravascular (CD31, gray); CD68+ macrophages (green) are intraparenchymal and perivascular in the naïve heart. CD68+ macrophages are closely associated to the microvasculature and in proximity to intracapillary B cells (yellow box). Blue stain, DAPI. Scale bar=10 μm. Data collected from 3 hearts (2 slices per heart). (B) Flow cytometric analysis of the cardiac macrophage pool as defined by CCR2 and MHC-II expression in wild-type (WT) and B cell-deficient (μMT) mice. Hearts from B cell-deficient mice display significantly lower numbers of CCR2−MHC-IIhigh macrophages than WT hearts. 5 hearts per condition. (C) Flow cytometric analysis of cardiac macrophage subpopulations in littermate mice treated with anti-CD20 B cell–depleting antibody or isotype control. B cell depletion was associated with reduced numbers of CCR2−MHC-IIhigh macrophages. Isotype control: 17 hearts; Anti-CD20: 17 hearts, except for CCR2−MHC-IIhi (15 hearts) and CCR2+MHC-IIlow (16 hearts). Outliers defined as experimental points two standard deviations away from the mean were excluded. Statistical comparisons between two groups were performed using two-tailed Student’s t-test, correcting for multiple comparisons with the Holm-Sidak method. Bars represent mean ± SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 (B-C).
