Fig. 1.
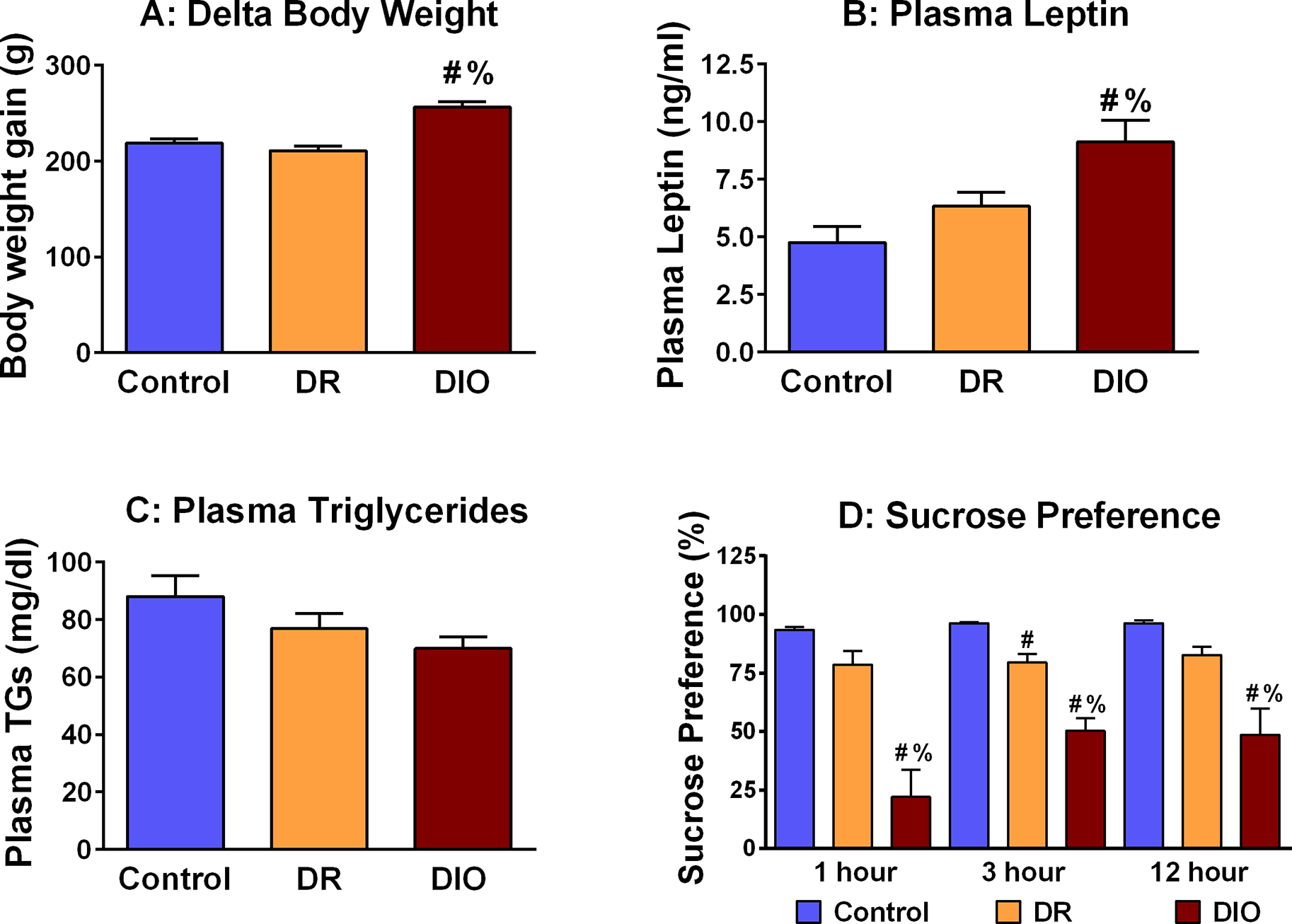
High fat diet exposure elicits an obesity and depressive-like phenotype in DIO, but not DR rats. (A) Cumulative body weight changes are significantly increased in DIO rats compared to DR rats and rats provided access to a control diet [F(2,18) = 22.44; p = 0.0001]. (B) DIO rats exhibit significant increases in plasma leptin levels compared to Control-chow rats and DR rats [F(2,18) = 8.754; p = 0.002]. (C) Plasma triglycerides are unchanged in Control rats, DR rats and DIO rats [F(2,18) = 2.626; p = 0.1]. (D) One-hour, three-hour and 12-hour sucrose preference was significantly decreased in DIO rats compared to Control rats and DR rats. Three-hour sucrose preference was also decreased in DR rats compared Control rats. One-hour [F(2,18) = 22.56; p = 0.001]; three-hour [F(2,18) = 32.26; p = 0.0001]; 12-hour [F(2,18) = 11.40; p = 0.0007] [# = p < 0.05 compared to control; % = p < 0.05 compared to DR]
