Figure 3-.
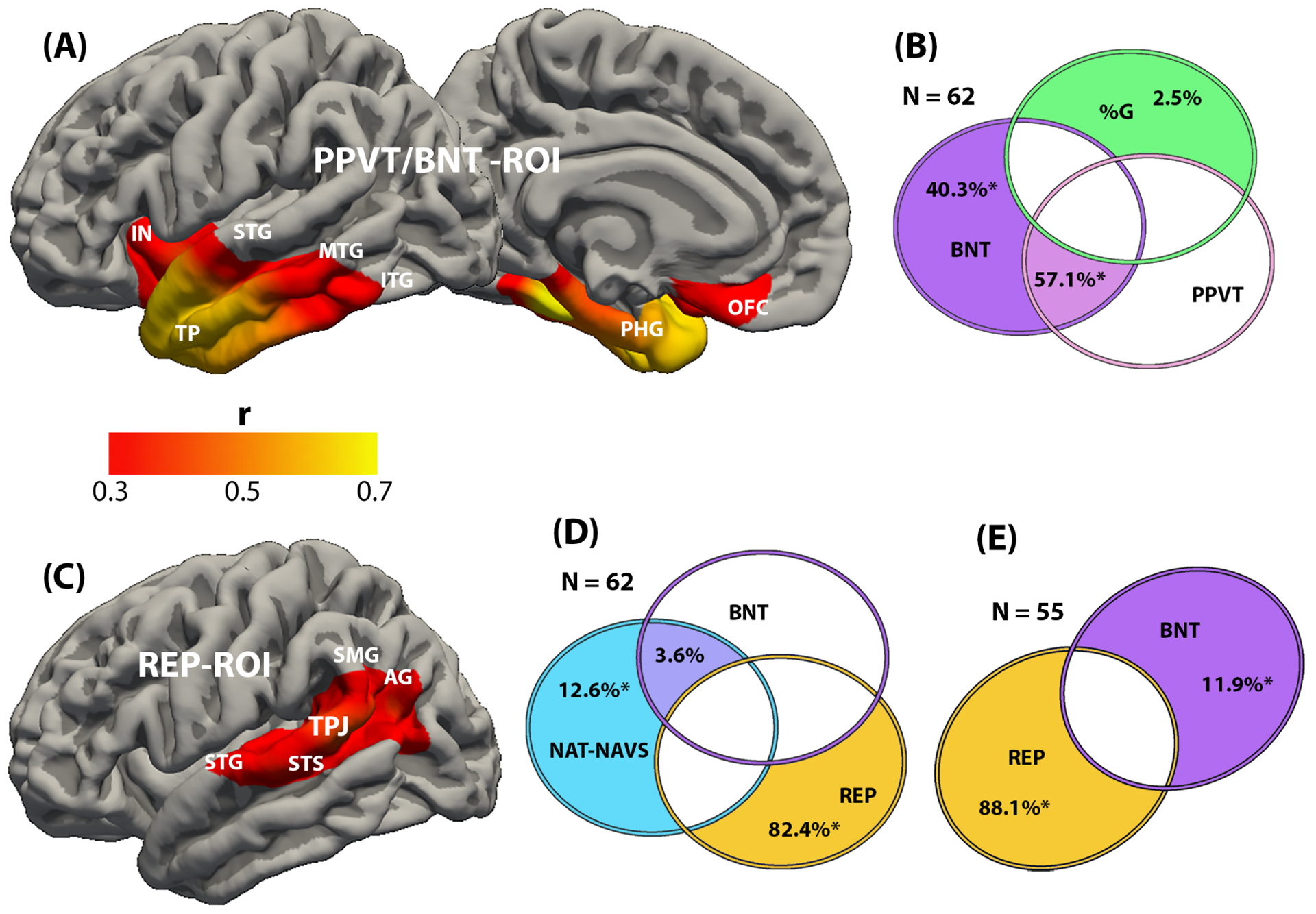
Results of the regression (A, C), and commonality (B, D) analyses in the cohort of 62 PPA participants. For the analysis in E, participants with the lowest scores of word comprehension (tested by the PPVT) were excluded to generate a subgroup of 55. A. The red and yellow areas indicate regions where cortical thinning (atrophy) was correlated with worse performance on the BNT and PPVT tests of object naming and single word comprehension (r range 0.3–0.743). The two tests led to regional correlations that were almost entirely overlapping. These areas are collectively designated PPVT/BNT-ROI. The heat map indicates the scale used to illustrate significance levels. B. Commonality analysis indicates the task-specific unique and shared contributions to the explained variance of thickness in the PPVT/BNT-ROI. Each circle reflects the contribution of a specific task, green for %G, orange purple BNT, magenta for PPVT. The numbers represent the percentage of contribution to the explained variance of the ROI. Overlapping areas represent shared contributions. Those with an asterisk were statistically significant. Absence of detectable contribution to variance of ROI thickness is indicated by the uncolored spaces. The figure offers a conceptual illustration of the results but is not drawn to scale so there is no correspondence between the magnitude of contribution and the areas encompassed by overlapping or non-overlapping parts of the circles. C. The red and yellow areas indicate regions where cortical thinning (atrophy) was correlated with impaired performance on the REP test of language repetition (r range 0.3–0.584). These areas are collectively designated REP-ROI. The heat map indicates the scale used to illustrate significance levels. D. Commonality analysis indicates the task-specific unique and shared contributions to the explained variance of thickness in the REP-ROI. Each circle reflects the contribution of a specific task, blue for NAT-NAVS, purple for BNT, gold for REP. The numbers represent the percentage of contribution to the explained variance of the ROI. Overlapping areas represent shared contributions. Those with an asterisk were statistically significant. Absence of detectable contribution to variance of ROI thickness is indicated by the uncolored spaces. The figure offers a conceptual illustration of the results but is not drawn to scale so there is no correspondence between the magnitude of contribution and the areas encompassed by overlapping or non-overlapping parts of the circles. E. Same analysis as in D but on a cohort of 55, including only those with a PPVT score above 60%. Abbreviations: AG- angular gyrus; BNT- test of object naming; %G- percentage of grammatically correct sentences in running speech; IN- insula; ITG- inferior temporal gyrus; MTG- middle temporal gyrus; NAT-NAVS- test of syntactically correct sentence construction; OFC- orbitofrontal cortex; PPVT- test of word comprehension; REP- test of language repetition; SMG- supramarginal gyrus; STG- superior temporal gyrus; STS- superior temporal sulcus; TPJ- temporoparietal junction.
