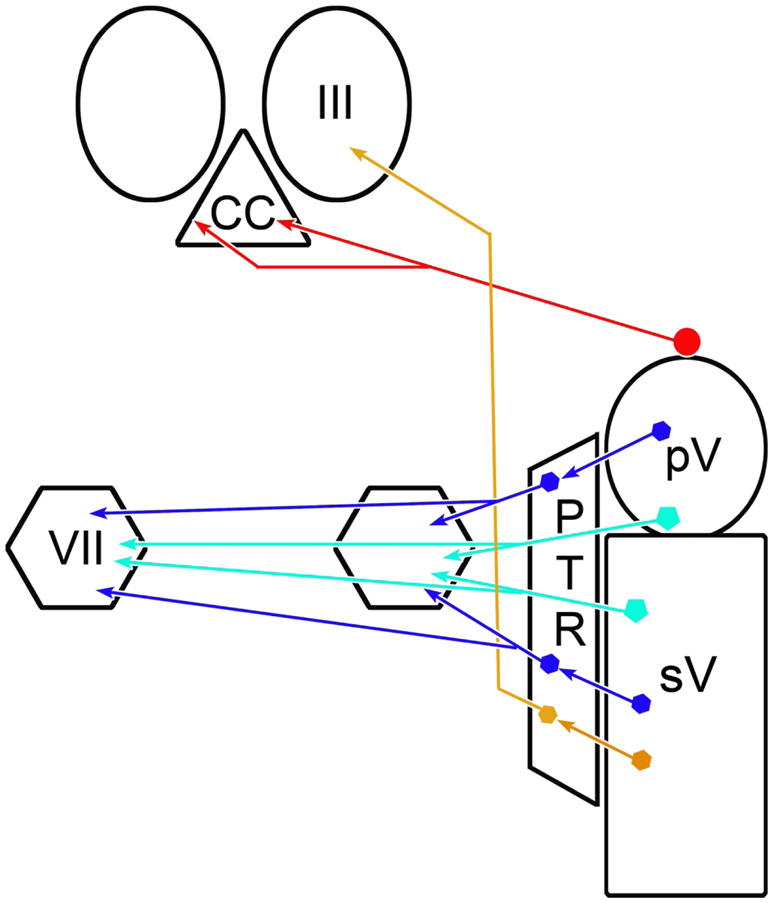
Figure 14.
Summary diagram showing trigeminal pathways underlying the blink reflex. The inhibitory trigemino-oculomotor pathway to the levator motoneurons located in the caudal central subdivision (CC) is shown in red. The monosynaptic excitatory pathways to the orbicularis oculi motoneurons in the facial nucleus (VII) are shown in light blue and the disynaptic excitatory pathways by way of the paratrigeminal reticular formation (PTR) are shown in dark blue [Data from May and Warren, 2021]. A putative excitatory pathway from the caudal portion of PTR to the oculomotor nucleus (III), which would cause retraction of the globe during a blink, is shown in brown.