Figure 2. mTORC1 activation with corresponding augmented protein synthesis rescues Rps6 haploinsufficiency phenotypes.
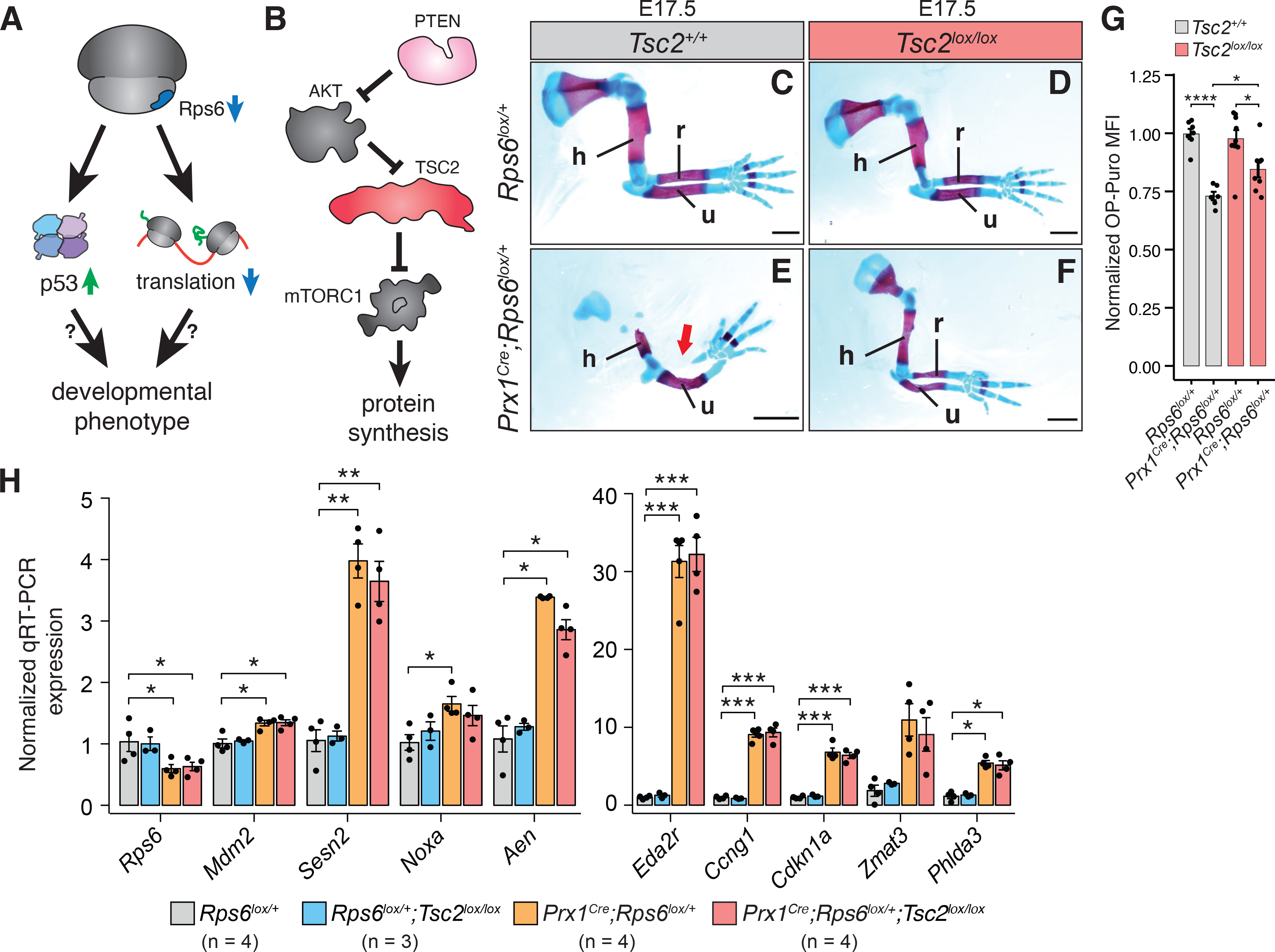
(A) Overview of potential pathways leading to developmental phenotypes upon Rps6 haploinsufficiency, specifically p53 activation and translation dysregulation.
(B) Schematic of mTORC1 regulation and downstream effects.
(C-F) Representative E17.5 forelimbs of WT (Rps6lox/+) and Prx1Cre;Rps6lox/+ embryos in Tsc2 WT (Tsc2+/+) or Tsc2 conditional loss (Tsc2lox/lox) backgrounds. Arrow indicates absence of radius. Scale bars, 1 mm.
(G) OPP MFI of cells dissociated from whole E10.5 forelimbs normalized to WT. n = 7 embryos, (Rps6lox/+;Tsc2+/+); n = 6 embryos, (Prx1Cre;Rps6lox/+;Tsc2+/+); n = 9 embryos, (Rps6lox/+;Tsc2lox/lox); n = 8 embryos, (Prx1Cre;Rps6lox/+;Tsc2lox/lox).
(H) RT-qPCR of p53 target genes from whole E10.5 forelimbs. n = 4 (Rps6lox/+, Prx1Cre;Rps6lox/+, Prx1Cre;Rps6lox/+;Tsc2lox/lox), n = 3 (Rps6lox/+;Tsc2lox/lox).
