Figure 3. p53 loss rescues Rps6 haploinsufficiency phenotypes, and p53 activation mediates translational changes upon Rps6 reduction.
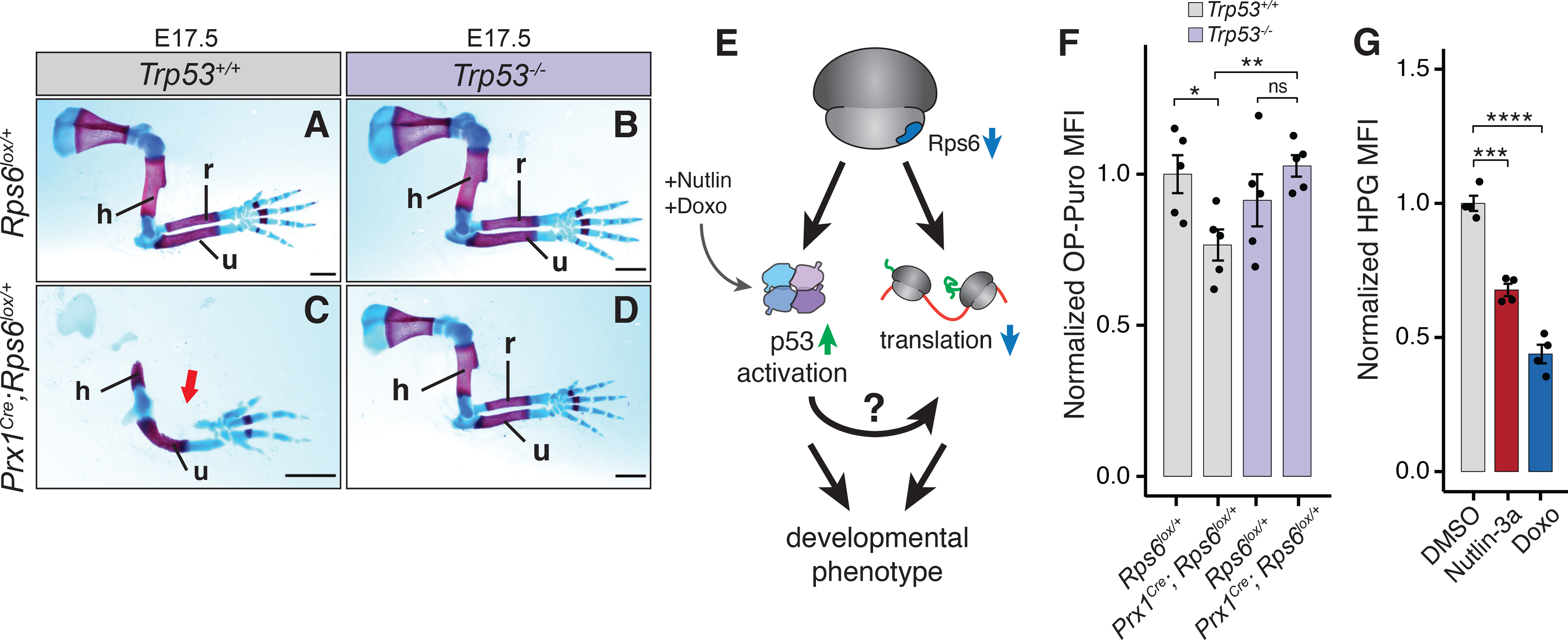
(A-D) E17.5 forelimbs of WT and Prx1Cre;Rps6lox/+ embryos in Trp53 WT (Trp53+/+) and Trp53 null (Trp53−/−) backgrounds. Arrow indicates absence of radius. Scale bars, 1 mm.
(E) Potential pathways for p53-dependent translational control upon Rps6 haploinsufficiency.
(F) OPP MFI of cells dissociated from whole E10.5 forelimbs normalized to WT (Rps6lox/+). n = 5 embryos.
(G) HPG MFI of mouse embryonic fibroblasts treated with Nutlin-3a or Doxo normalized to DMSO treated control. 8 h treatment, n = 4.
