Figure 5. p53 activation leads to transcriptional upregulation of Eif4ebp1.
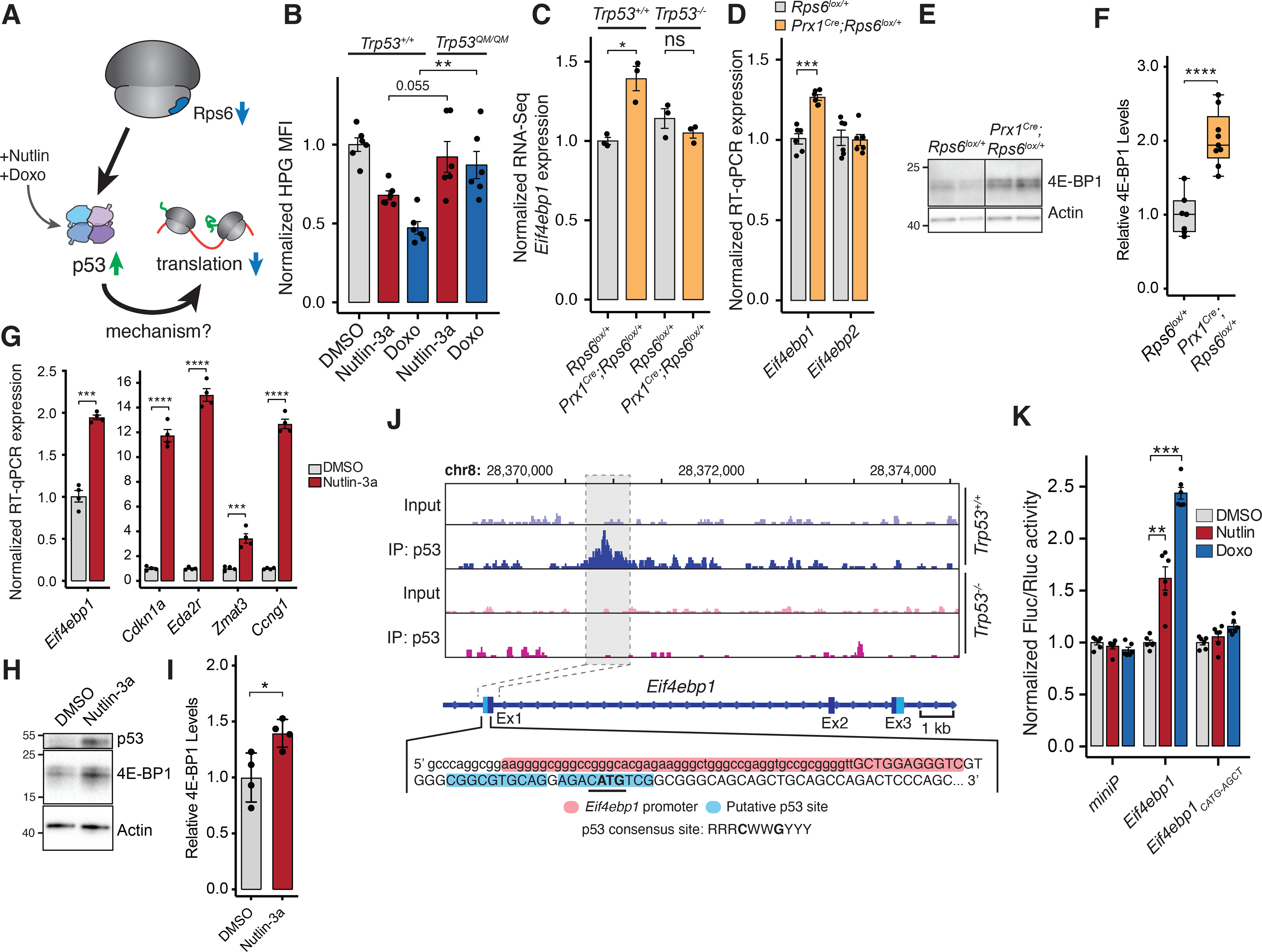
(A) Potential model of p53-dependent translational control upon Rps6 haploinsufficiency.
(B) HPG MFI of MEFs expressing WT or transactivation dead p53 (Trp53QM) treated with Nutlin-3a or Doxo normalized to mean of DMSO control expressing WT p53. 8 h treatment, n = 6.
(C) Eif4ebp1 expression from RNA-Seq of whole E10.5 forelimbs normalized to WT (Rps6lox/+;Trp53+/+), n = 3.
(D) Expression of Eif4ebp1 and Eif4ebp2 mRNA from whole E10.5 forelimbs.
(E-F) Representative 4E-BP1 Western blot (E) and quantification (F) from Figure S7B of E10.5 Rps6lox/+ and Prx1Cre;Rps6lox/+ forelimb mesenchyme cells after ectoderm removal with values normalized to Actin and Rps6lox/+. n = 7, Rps6lox/+; n = 9, Prx1Cre;Rps6lox/+.
(G) Expression of Eif4ebp1 and p53 target genes by RT-qPCR from NIH3T3 cells treated with DMSO or Nutlin-3a for 8 h.
(H-I) Western blot of 4E-BP1 from NIH3T3 cells treated with Nutlin-3a for 8 h. Shown is a representative blot (H) with quantification (I) from 4 independent replicates.
(J) p53 ChIP-Seq gene track of Eif4ebp1 locus (Kenzelmann Broz et al., 2013) from Doxo-treated Trp53+/+ and Trp53−/− MEFs. Capital letters = transcription state site; red highlight = Eif4ebp1 promoter; blue highlight = putative p53-binding region; bold = Eif4ebp1 start codon; underline = p53 core binding sequence.
(K) Fluc/Rluc activity normalized to DMSO control of each construct. Plasmid containing a minimal promoter, the Eif4ebp1 region, or mutated Eif4ebp1 region (Figure S7F) were transfected into NIH3T3 cells and treated with DMSO, Nutlin-3a, or Doxo for 8 h; n = 6.
