Figure 6. p53 controls translation in part through 4E-BP1.
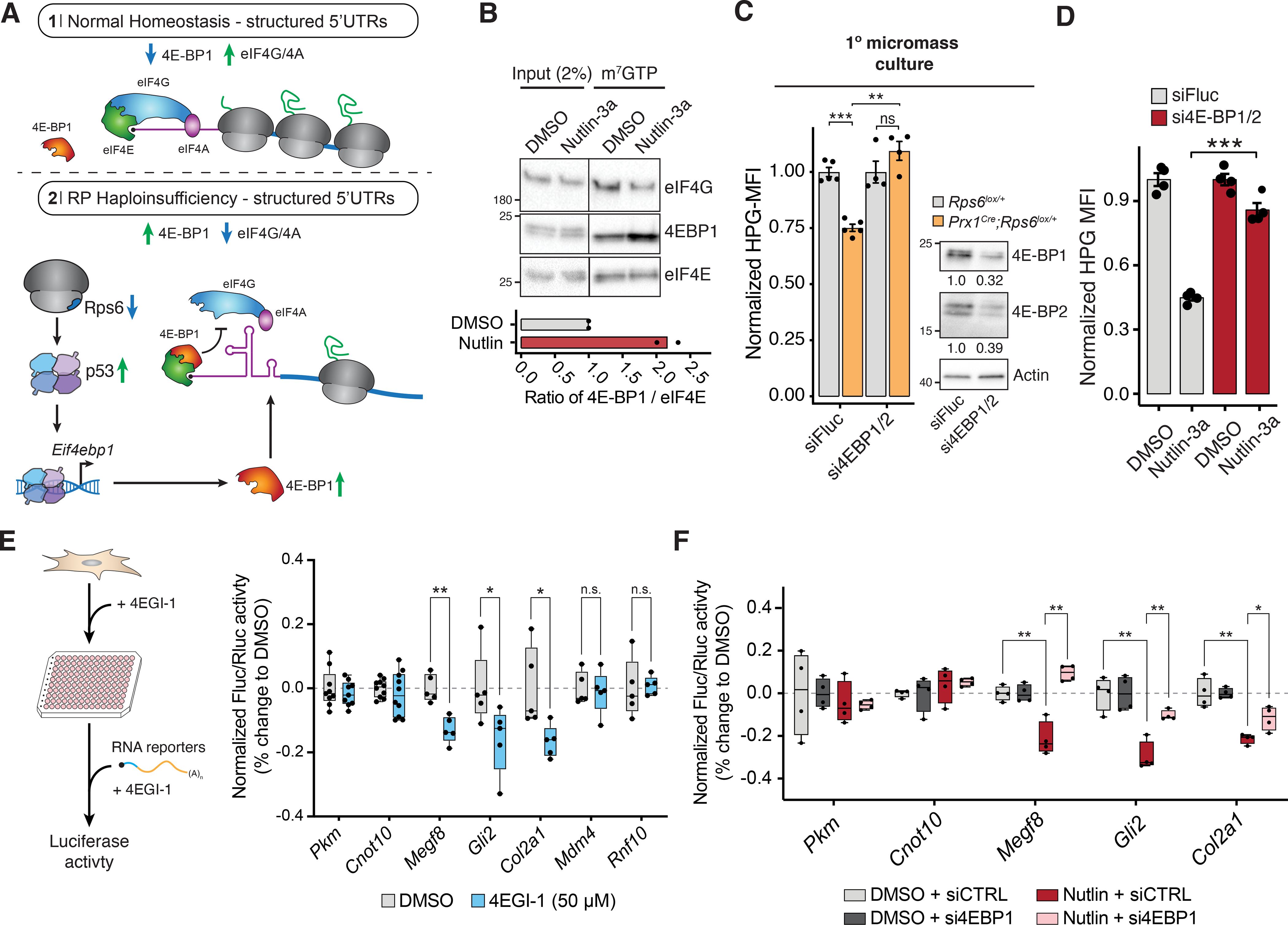
(A) mRNAs with highly structured 5’UTRs are particularly sensitive to eIF4E/4E-BP1-mediated regulation (Pelletier and Sonenberg, 1985; Pelletier et al., 2015). In normal homeostasis (1), eIF4E recruits eIF4G/4A, which helps unwind structured 5’UTRs and promote translation. Upon RP haploinsufficiency (2), p53-mediated 4E-BP1 induction may lead to selective translational repression of structured mRNAs by blocking eIF4E-eIF4G/4A binding.
(B) Cap-binding assay of NIH3T3 cells treated with Nutlin-3a for 8 h. Bottom: ratio of 4E-BP1 to eIF4E in cap-binding assays; n = 2.
(C) Left: HPG MFI upon 4E-BP1/2 siRNA treatment in primary Rps6lox/+ and Prx1Cre;Rps6lox/+ limb micromass cultures from whole E10.5 forelimbs. Values normalized to respective wildtype of each siRNA condition; n = 4. Right: Western blot of 4E-BP1 and 4E-BP2 levels in primary Rps6lox/+ limb micromass cultures after siRNA treatment for 16 h. Numbers indicate quantification of proteins normalized to siFluc.
(D) HPG MFI upon 4E-BP1/2 siRNA treatment in NIH3T3 cells normalized to mean of respective DMSO control for each knockdown condition; n = 4.
(E) Left: Schematic of 4EGI-1 treatment and luciferase RNA reporter assay in C3H/10T1/2 mesenchymal cells. Right: Fluc/Rluc activity of RNA reporters transfected into C3H/10T1/2 cells after 4 h 4EGI-1 treatment. Activity was normalized to the geometric mean of Pkm and Cnot10 5’UTR reporters and mean of DMSO control.
(F) Fluc/Rluc activity from transfection of RNA reporters in NIH3T3 cells treated with either DMSO or Nutlin-3a for 8 h after siRNA knockdown for 16 h with control or 4E-BP1 siRNA. Activity was normalized to the geometric mean of control Pkm and Cnot10 5’UTR activities and mean of respective DMSO control of each knockdown condition.
