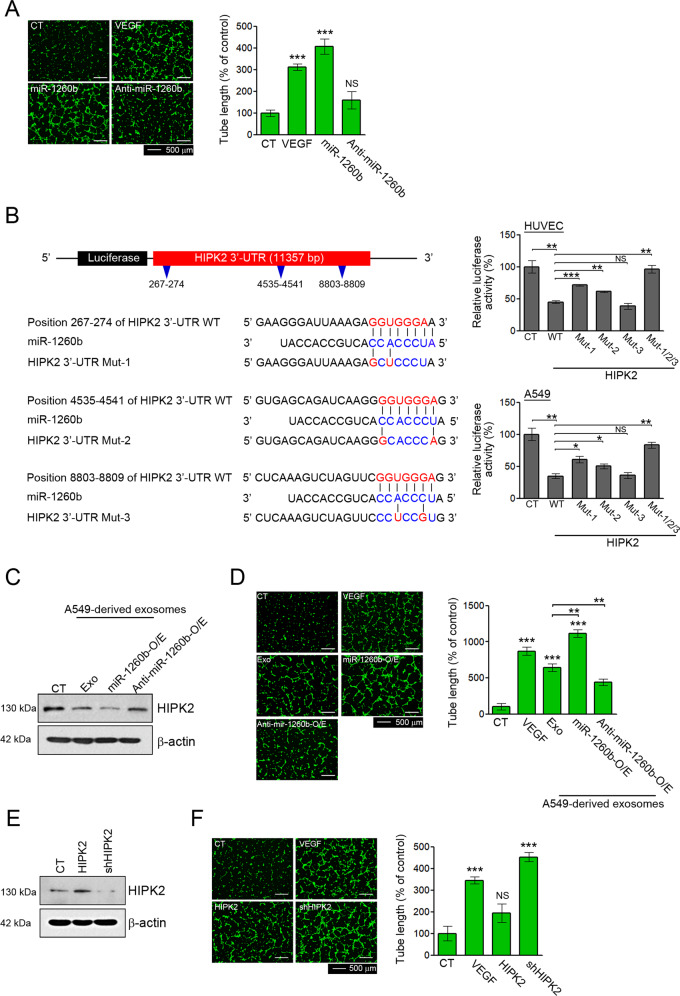
Fig. 1. Effects of exosomal miR-1260b on angiogenesis via direct modulation of HIPK2.
A HUVECs were treated with 40 ng/mL VEGF, a 50 nM miR-1260b mimic, and a miR-1260b inhibitor. Effect of miR-1260b on the tube formation ability was determined by tube length. Tube lengths were measured using ImageJ software. B Schematic diagram of the putative miR-1260b-binding site within the 3′UTR of HIPK2. The seed sequence of miR-1260b matches three predicted target sites (nucleotides 267–274, 4535–4541, and 8803–8809; red). Five nucleotides within each target site complementary to the seed sequence (nucleotides 2–7 of miRNA) of miR-1260b were mutated in the HIPK2 3′UTR-mutant plasmids including single (Mut-1: 267–274, Mut-2: 4535–4541, and Mut-3: 8803–8809) or triple (Mut-1/2/3: 267–274, 4535–4541, and 8803–8809) mutants. The number indicates the position of the nucleotides in the wild-type (WT) sequence of the HIPK2 3′UTR site. For the dual-luciferase assay, luciferase activities of plasmids with WT or Mut sequence of HIPK2 were assessed in HUVECs and A549 cells co-transfected with miR-1260b mimic, and then Renilla luciferase activity was calculated as the luciferase activity ratio of firefly to Renilla luciferase. C–F HUVECs were treated with 40 ng/mL VEGF, 50 μg of exosomes derived from A549, and their stable cell lines (miR-1260b-O/E and Anti-miR-1260b), lentiviral HIPK2 or shHIPK2. D, F Tube lengths were measured using ImageJ software. C, E HIPK2 expression was confirmed by western blotting. All data are reported as the mean ± standard deviation. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0005 compared with the control group.