Figure 5.
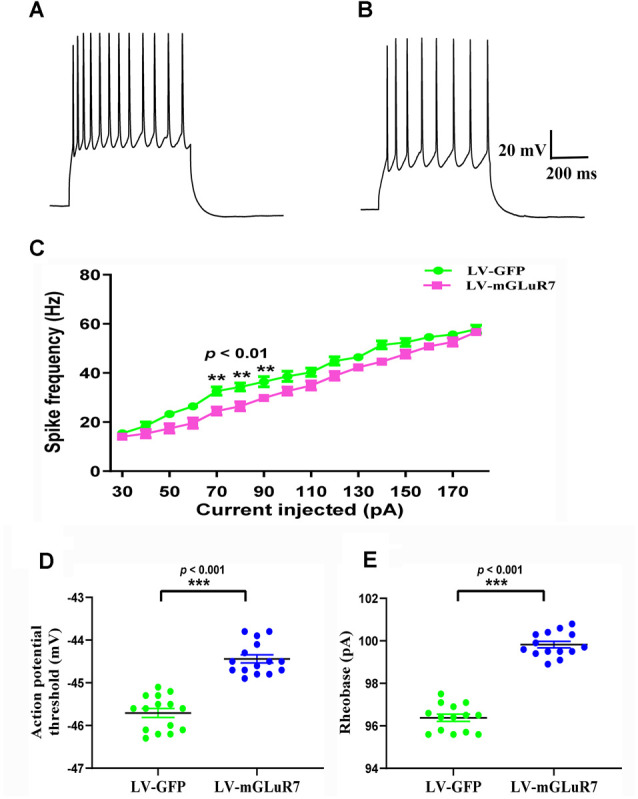
In vitro whole-cell recordings revealing the impact of mGluR7 on neuronal excitability in PFC slices. (A,B) Representative GFP-positive and mGluR7-expressing neurons traces corresponding to firing frequencies following the intracellular injection of step currents in mice exposed to VPA administered LV-GFP or LV-mGluR7. (C) Evoked spike rates vs. pyramidal cell current magnitudes in the PFC in the two treatment groups, exhibiting a significant reduction in mean firing frequency in LV-mGluR7-injected mice relative to controls (F(1,28) = 11.023, p < 0.01; F(1,28) = 10.058, p < 0.01; F(1,28) = 8.129, p < 0.01). n = 8 animals per group. **p < 0.01; repeated measures ANOVA. Data are means ± SEM. (D,E) The action potential threshold of LV-mGluR7-exposed mice was significantly higher than those of LV-GFP-treated mice (p < 0.001). The rheobase of LV-mGluR7-exposed mice was significantly greater than those of controls (p < 0.001). n = 7 animals in each group. ***p < 0.001; Student’s t-test. Data are presented as means ± SEM.
