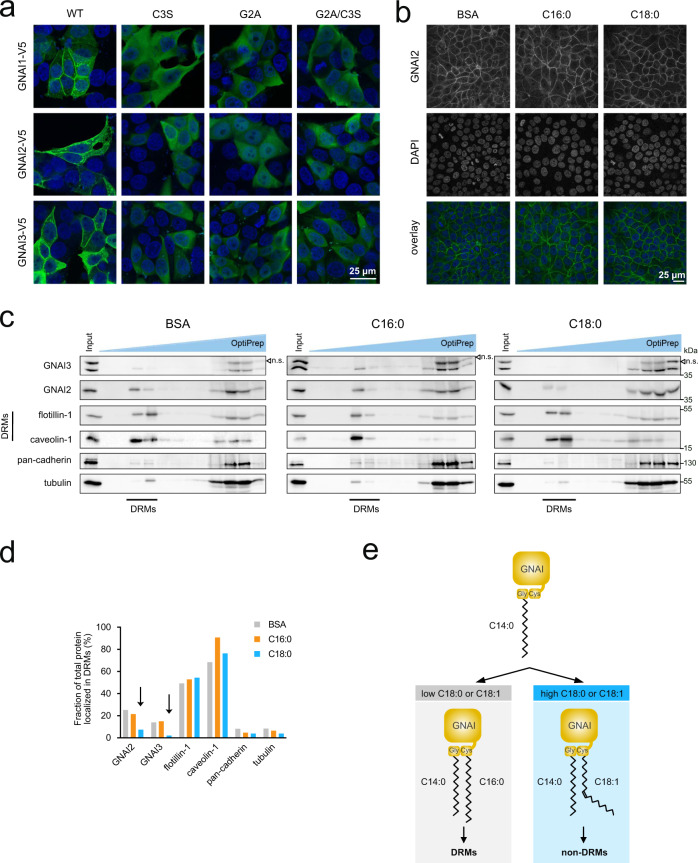
Fig. 4. Exposure of cells to C18:0 shifts GNAI proteins out of detergent-resistant membranes (DRMs).
a S-acylation of GNAI proteins is required for their membrane localization. Unlike wild-type (WT) GNAI proteins, GNAI mutants lacking S-acylation do not localize to the plasma membrane, detected by immunostaining (green: anti-V5, blue: DAPI, scale bar 25 μm). Representative of three biological replicates. b Exposure of cells to C18:0 or C16:0 does not alter the localization of endogenous GNAI2 to the cell membrane, detected by immunostaining (green: anti-GNAI2, blue: DAPI, scale bar 25 μm). Representative of two biological replicates. c, d Endogenous GNAI2 and GNAI3 are depleted from DRMs upon exposure of cells to C18:0 but not C16:0. DRMs are isolated by the protein flotation assay in discontinuous OptiPrep gradients after solubilization with 1% Triton X-100 (c). As markers of DRMs, flotillin-1 and caveolin-1 were used. Quantification of the relative amount of each protein in DRMs normalized to total cell content of that protein (sum of all fractions) is shown in (d). Representative of three biological replicates. e Schematic diagram summarizing the findings presented here on GNAI S-acylation.