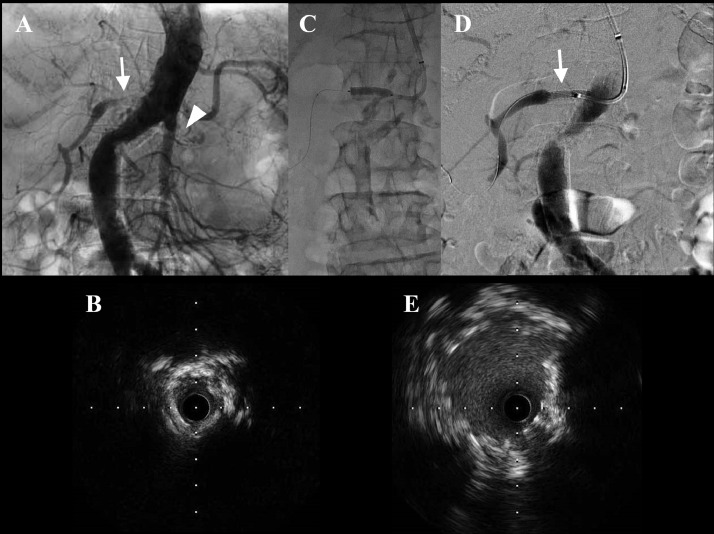
Fig. 2.
Aortography showed severe ostial stenosis of the right renal artery (arrow) and suboccluded left renal artery (arrowhead) (A). RAS was performed after predilatation of balloon (C), and the right renal artery was expanded well (arrow) (D). Intravascular ultrasound imaging revealed obstructive deposition of heterogeneous intimal plaques with marked calcification before RAS (B) and adequate vessel dilatation of a minimal luminal diameter of 4.6 mm after RAS (E) at the ostium of the right renal artery. RAS, renal artery stenting.