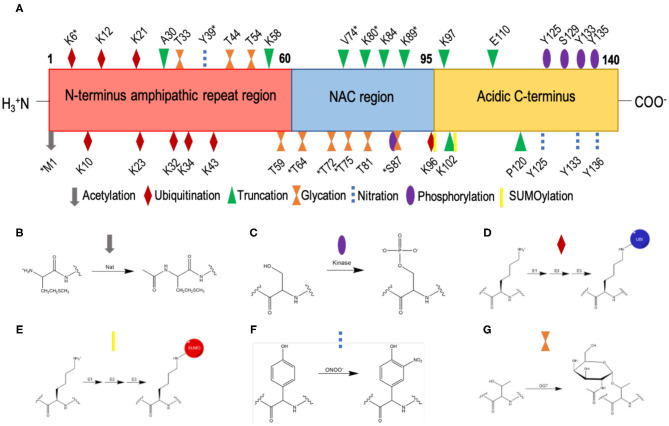
Figure 4.
List of currently known post-translational modifications of α-synuclein. (A) The amino acid sequence of α-synuclein comprises an N-terminal amphipathic region (residues 1-60), a non-Aβ component (NAC) region (residues 61-95), and an acidic C-terminal region (residue 96-140). Post-translation modification sites are labelled; *indicates post-translation modifications within low-solubility areas using CamSol (70). (B) N-terminal acetylation, which is carried out by N-acetyltransferases (Nat). (C) Phosphorylation, which occurs by the esterification by a phosphate group of the side-chain hydroxyl moiety of serine or threonine residues; shown here is the phosphorylation of a serine residue. (D) Ubiquitination, where ubiquitin is added to lysine residues via an isopeptide bond, catalysed by sequential action of 3 enzymes, E1 (ubiquitin-activating enzyme), E2 (ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme) and E3 (ubiquitin ligase). (E) SUMOylation, where SUMO is added to lysine residues via a thioester bond, catalysed by sequential action of 3 enzymes, E1 (SUMO-activating enzyme), E2 (SUMO-conjugating enzyme), and E3 (SUMO ligase). (F) Nitration, where tyrosine residues are nitrated by peroxynitrite; the phenolic R group is converted to 3-nitro-tyrosine, by the addition of a nitro (NO2) group onto the ortho position of the ring by peroxynitrite. (G) O-GlcNAcylation, where the enzyme O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) catalyses the addition of N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) to the hydroxyl group (O-linked) of the side-chains of serine and threonine residues; shown here is the O-GlcNAcylation of a threonine residue.