Figure 13.
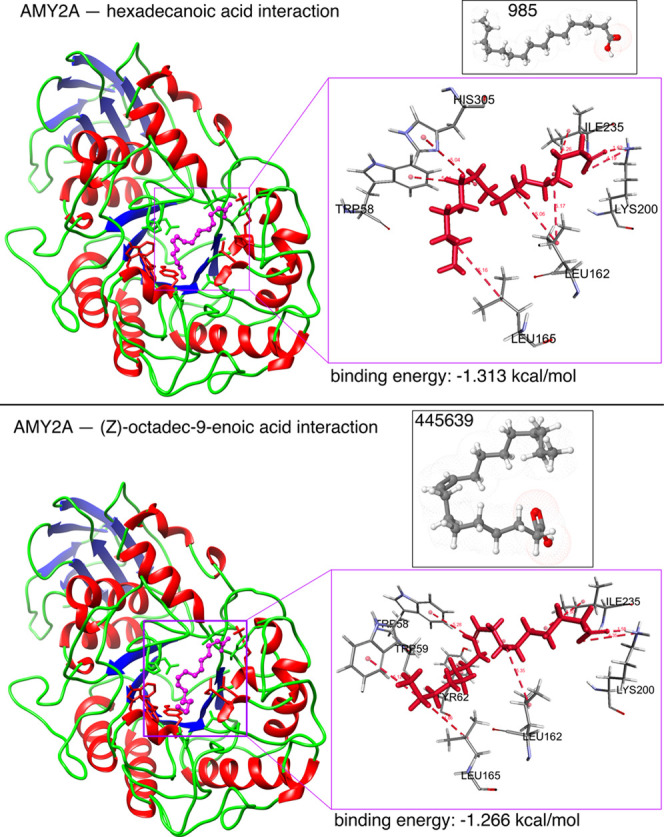
In silico α-amylase docking analyses with hexadecanoic acid and (Z)-octadec-9-enoic acid. The α-amylase protein structure is shown as a brown backbone ribbon, and the compounds are indicated with sticks. Interacting residues were determined using BIOVIA Discovery Studio Visualizer (Dassault Systems K.K., Tokyo, Japan);54 hydrogen bonds are represented by pale red dotted lines. Docking was performed using Glide 4.0 (XP) extra precision (Schrödinger) to depict the binding mode and calculate binding energies as described previously.55−57 Hexadecanoic acid interacted with surrounding residues through hydrophobic interactions with TRP59, TYR62, GLN63, TYR151, THR163, HIS201, GLU233, and GLY306; H-bonds with LYS200; and π–π interactions with TRP58, LEU162, and LEU165. (Z)-Octadec-9-enoic acid interacted with surrounding residues through hydrophobic interactions with TRP59, TYR62, GLN63, TYR151, THR163, HIS201, GLU233, ASP300, and GLY306; H-bonds with LYS200; and π–π interactions with TRP58, LEU162, and LEU165.
