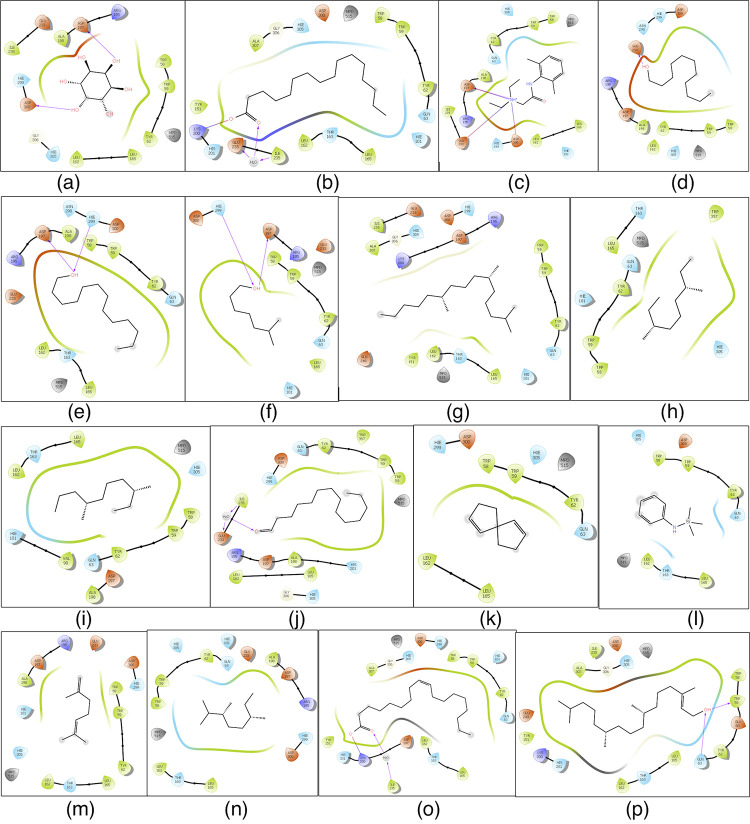
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of 2D interactions of α-amylase with select phytochemicals identified in the ethanolic (70%) leaf extract of L. leucocephala. (a) Cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol; (b) hexadecanoic acid; (c) 2-(diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide; (d) undecan-1-ol; (e) tridecan-1-ol; (f) 6-methylheptan-1-ol; (g) 2,6,10-trimethylpentadecane; (h) 3,7-dimethylnonane; (i) 3,7-dimethyldecane; (j) tetradecanal; (k) spiro[4.4]nona-3,8-diene; (l) N-trimethylsilyl aniline; (m) 2,6-dimethylhepta-1,5-diene; (n) 2,3,6-trimethyloctane; (o) (Z)-octadec-9-enoic acid; and (p) (E)-3,7,11,15-tetramethylhexadec-2-en-1-ol. Black lines indicate C–C (chemicals) or peptide bonds (protein). Amino acid color code indicates hydrophobicity and polarity. Van der Waals forces/hydrogen bonds are indicated by colored arrows. Hexadecanoic acid and (Z)-octadec-9-enoic acid interact with key AAs in the active site of α-amylase.16