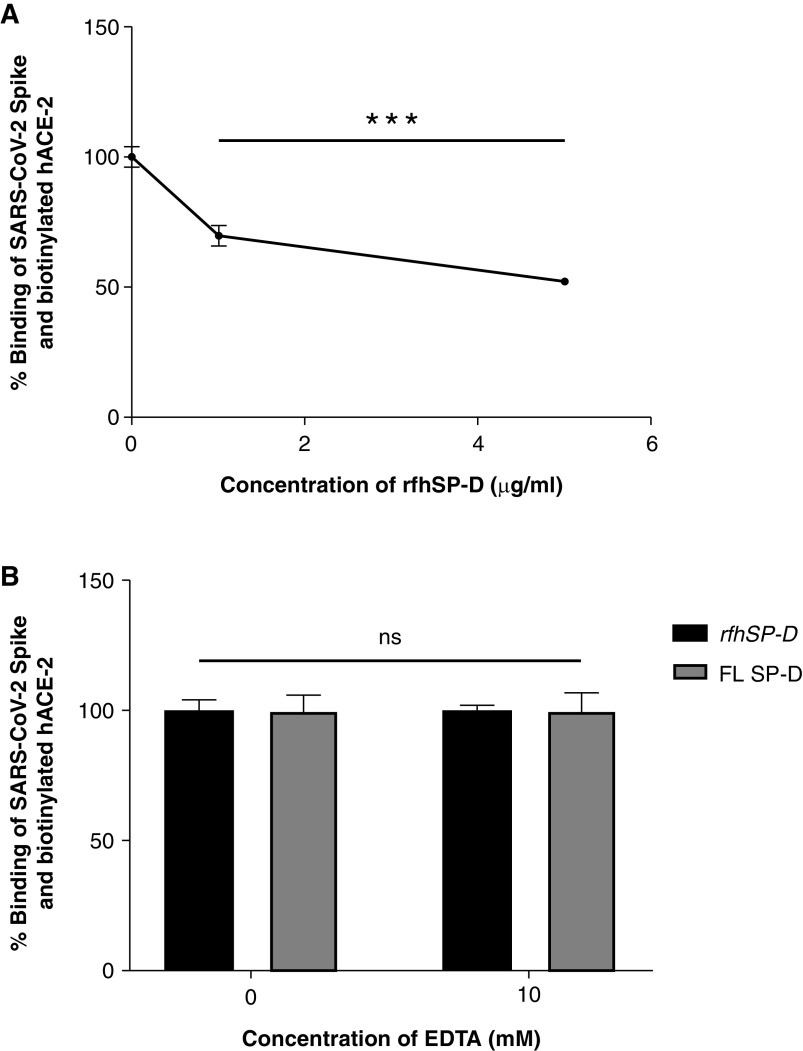
Figure 4.
rfhSP-D inhibits the interaction between S protein of SARS-CoV-2 and biotinylated hACE-2 in a calcium-independent manner (A and B). Microtiter wells were coated with 0.3 μg/ml (0.54 nM) of S protein. (A) After blocking, rfhSP-D (5, 1, and 0 μg/ml or 83.5, 16.7, and 0.0 nM) was added and incubated for 1 hour, followed by probing with biotinylated hACE-2. (B) To assess the effect of calcium in the SP-D–mediated inhibition of S protein–hACE-2 interaction, 5 μg/ml or 83.5 nM of rfhSP-D and FL SP-D (5 μg/ml or 9.5 nM) with or without 10 mM EDTA was added. BSA (5 μg/ml) was used as nonspecific protein control (mean of the normalized triplicates ± SEM = 0.297 ± 0.005). S protein–hACE-2 binding was detected with streptavidin-HRP. Background was subtracted from all data points. The data were normalized with 100% S protein–hACE-2 binding being defined as the mean of the absorbance recorded from the control sample (0 μg/ml rfhSP-D). The data were presented as the mean of the normalized triplicates ± SEM. Significance was determined using the one-way ANOVA (n = 3). ***P < 0.0001.