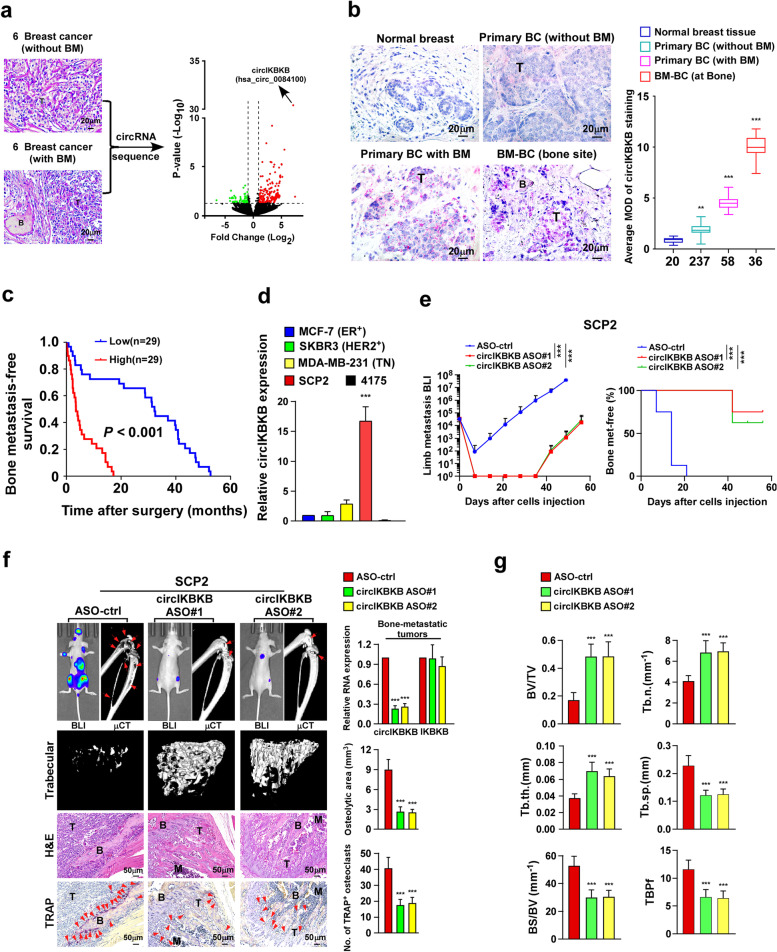
Fig. 1.
Silencing circIKBKB inhibits osteolytic bone metastasis of breast cancer in vivo. a H&E analysis (left) and Volcano plot analysis (right) of dysregulated circRNAs from circRNAs deep sequencing comparing BC tissues with or without bone metastasis (n = 6). b ISH analysis (left) and quantification (right) of circIKBKB expression in 20 normal breast tissues and 331 clinical BC tissues, including 295 primary BC tissues (237 non-BM/BC and 58 BM/BC) and 36 bone-metastatic BC tissues (at bone). c Kaplan–Meier analysis of bone metastasis-free survival curves in patients with BM/BC with low vs high expression of circIKBKB (n = 58; P < 0.001, log-rank test). d Real-time PCR analysis of circIKBKB expression in the indicated cells. GAPDH served as a loading control. e Normalized BLI signals of bone metastases and Kaplan–Meier bone metastasis-free survival curve of mice from the indicated experimental groups (n = 8/group). f Left: BLI, μCT (longitudinal and trabecular section) and histological (H&E and TRAP staining) images of bone lesions from representative mice. Scale bar, 50 μm. Right: Quantification of circIKBKB and IKBKB expression and μCT osteolytic lesion area and TRAP+ osteoclasts along the bone-tumor interface of metastases from experiment in the left panel. g Quantification of bone parameters from representative mice in (g). BV/TV, bone/tissue volume ratio; BS/TV, bone surface/ tissue volume ratio; Tb. n, trabecular number; Tb. sp., trabecular separation; Tb. th., trabecular thickness; TBPf, trabecular bone pattern factor. Each error bar represents the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001