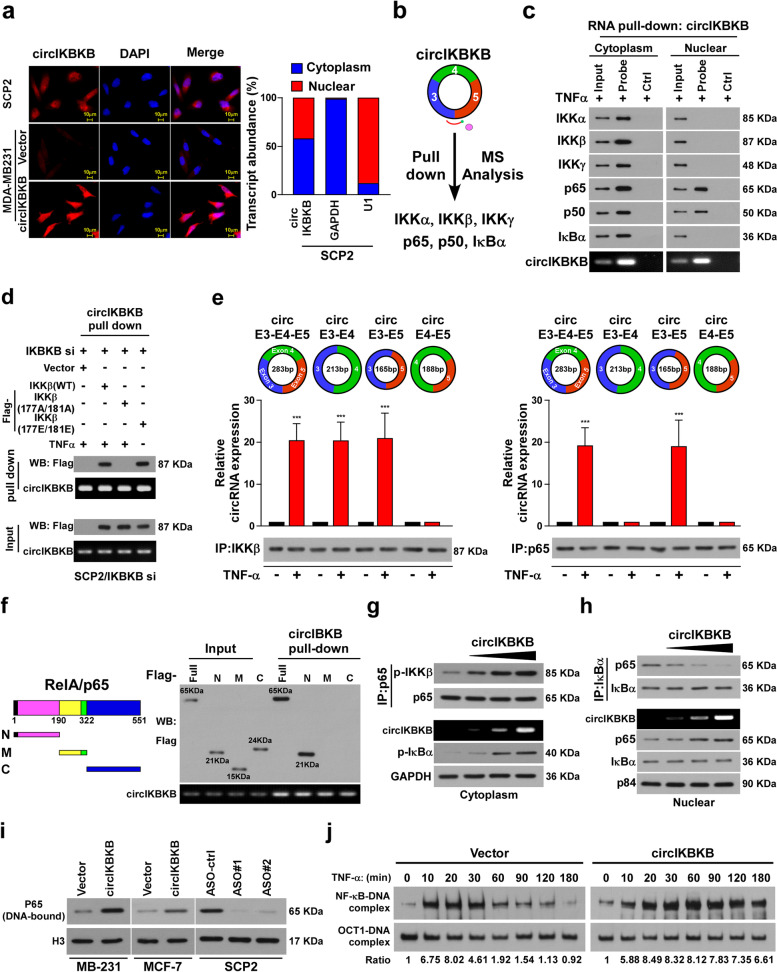
Fig. 4.
Cytoplasmic circIKBKB facilitates IKKβ-mediated IκBα phosphorylation and nuclear circIKBKB inhibited IκBα feedback loop. a FISH (left) and qPCR from nuclear-cytoplasmic fractionation analysis of subcellular localization of circIKBKB. b circIKBKB pull-down following the mass spectrometry showed that circIKBKB interacted with IKKα/IKKβ/IKKγ and p65/p50/IκBα complex. c RNA pull-down assay analysis of cytoplasmic and nuclear circIKBKB-interacting proteins (“probe” stands for circIKBKB probe, “Ctrl” stands for control probe). d RNA pull-down assay showing that circIKBKB only bound to active IKKβ. e RIP assay analysis of the binding region of circIKBKB with IKKβ or p65. f Schematic illustration of Flag-tagged full-length p65 and three truncated p65 fragments (left) and RNA pull-down assay analysis(right) of interaction between circIKBKB with p65 fragments. g IP (upper) and WB (lower) analysis showing that cytoplasm circIKBKB facilitated IKKβ/p65 interaction and IKKβ-mediated IκBα phosphorylation in a dose dependent manner. GAPDH served as loading control. h IP (upper) and WB (lower) analysis showing that nuclear circIKBKB inhibited IκBα feedback loop. P84 served as loading control. i Chromatin fraction and WB analysis of DNA-bound NF-κB in the indicated cells. H3 served as a loading control. j EMSA analysis of NF-κB activity in the indicated MDA-MB-231 cells treated with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for the indicated times. Each error bar represents the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001