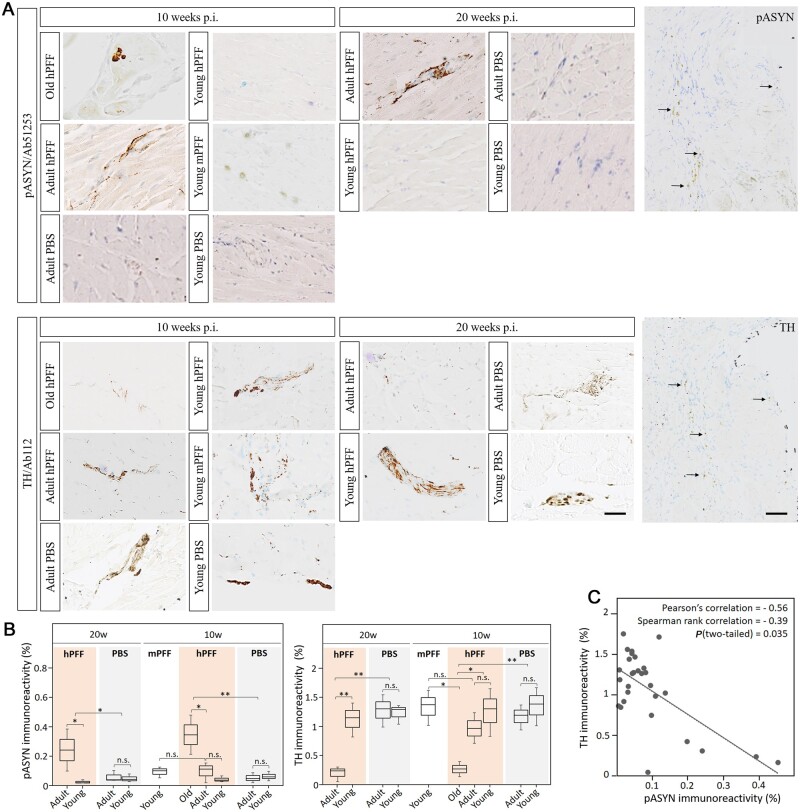
Figure 6.
Age-dependent phosphorylated α-syn pathology (Ab51253) in the myocardium of seeded and age-matched control rats. (A) High magnification micrographs of α-syn pathology (pASYN, top) and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH, bottom) in myocardial ganglia of old, late adult and young rats at 10 and 20 weeks post-injection (p.i.) with hPFF or mPFF. α-Syn pathology seems to be age-dependent, progressive and co-localized with TH. Scale bars = 20 µm and 50 µm. (B) Quantitative assessment of phosphorylated α-syn (pASYN) and noradrenergic innervation (TH) in the heart detected with immunohistochemistry. Adult (at 20 weeks post-injection) and old (at 10 weeks post-injection) hPFF-injected rats show more pathology than young hPFF-injected and age-matched control rats in the heart (P < 0.05). Noradrenergic innervation is decreased in hPFF-seeded old rats (at 10 weeks post-injection) and late adult rats (at 20 weeks post-injection) (C) Correlation plot of TH and pASYN immunoreactivity indicates a negative correlation between α-syn pathology and noradrenergic innervation in the heart. (P < 0.05). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; n.s. = not significant.