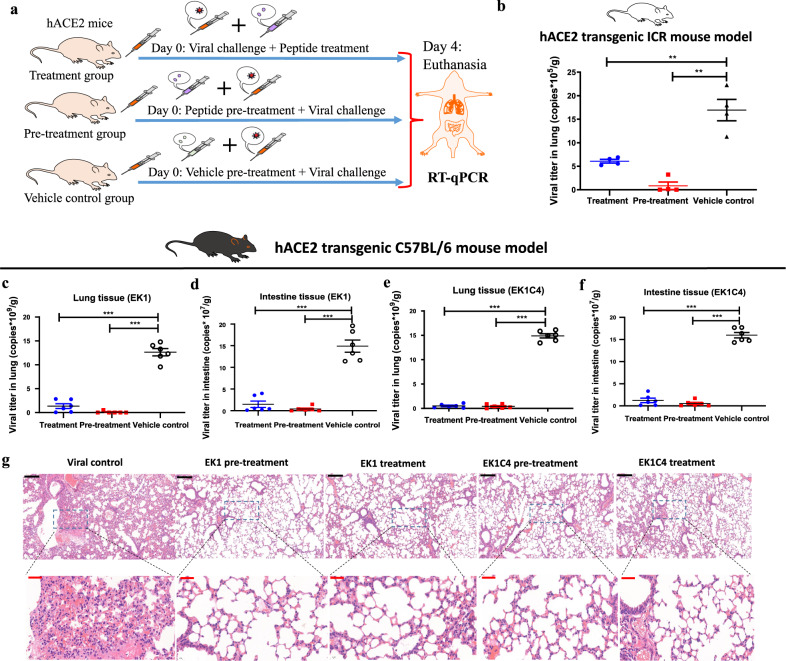
Fig. 3.
In vivo prophylactic and therapeutic efficacy of EK1 peptides against SARS-CoV-2 infection in hACE2 transgenic mouse models. a Schematic diagram of EK1 or EK1C4 administration and SARS-CoV-2 challenge. The mice in the treatment group were nasally administrated with a test peptide 30 min after challenge with SARS-CoV-2. The mice in the pre-treatment group and vehicle control group mice were nasally treated with a test peptide or vehicle control, respectively, 30 min before challenge with SARS-CoV-2. b Anti-SARS-CoV-2 efficacy of EK1 (200 μg/mouse) in hACE2 transgenic ICR mouse model. Viral titer in lung tissue of mice in each group on the 4th day of post-infection was detected. c, d Anti-SARS-CoV-2 efficacy of EK1 (200 μg/mouse) in vivo on hACE2 transgenic C57BL/6 mouse model. Viral titer in mouse lung (c) or intestine (d) of each group on the 4th day of post-infection was detected. e, f Anti-SARS-CoV-2 potency of EK1C4 (10 μg/mouse) in vivo on hACE2 transgenic C57BL/6 mouse model. Viral titer in lung (e) or intestine (f) of mice in each group on 4th day after SARS-CoV-2 challenge was detected. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. g Histopathological examination of lung tissue of Tgtn(CAG-human ACE2-IRES-Luciferase) mice with or without administration of EK1 peptides. Lungs from hACE2 transgenic C57 mice were collected on the day 4 of post-infection. The lung tissue sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin for histopathological examination. Scale bars in black, 200 μm (upper), scale bars in red, 40 μm (bottom)