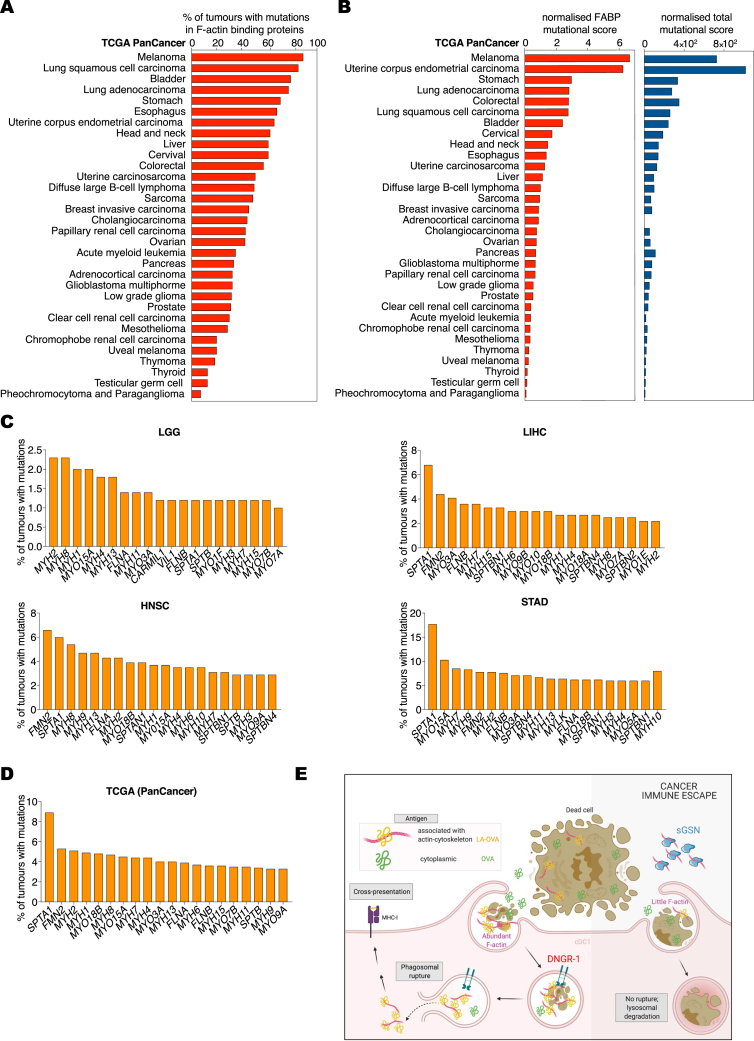
Figure S7.
Prevalence of mutations in F-actin-binding proteins in human cancers, related to Figure 7
(A) Mutational prevalence presented as percentage of tumors with ≥ 1 mutation in F-actin binding proteins in the indicated TCGA datasets.
(B) Normalized F-actin binding proteins (FABP; left) or total (right) mutational scores are defined as number of mutations per number of tumors in the indicated TCGA datasets.
(C and D) Top 20 frequently mutated F-actin binding proteins (C) as percentage of total mutation count of tumors in LGG, LIHC, HNSC, STAD datasets and (D) as percentage of total mutation counts of tumors among all the TCGA datasets listed in (A and B).
(E) Schematic summary of the findings: sGSN in the TME promotes cancer immune evasion by inhibiting F-actin binding to DNGR-1, thus, leading to impairement of phagosomal rupture in cDC1 and subsequent cross-presentation preferentially of neoantigens associated with actin cytoskeleton. Image was generated with BioRender.