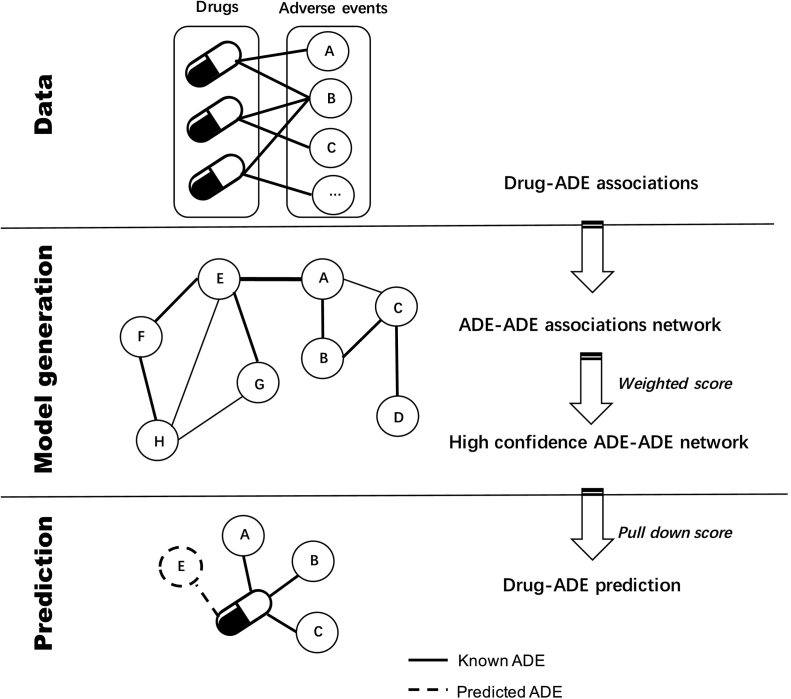
Fig. 1.
Workflow of the computational systems toxicology approach to predict adverse drug events (ADE) of drugs. Data: As a first step, drug-ADE associations were extracted from the DrugCentral database (http://drugcentral.org/ (accessed March 10, 2020). Model generation: An ADE-ADE network model was created based on the compiled data, in which two ADEs were connected if they shared at least one drug. For each ADE pair, a weighted score (wS) was calculated in order to highlight the most significant ADE-ADE associations. Prediction: for a given drug, the known ADEs were automatically screened against the ADE-ADE network. To quantify the prediction, and prioritize drug-ADE associations finding through the network, a pull-down score (pullS) was calculated between known ADE and its first order interacting ADEs present in the developed model.