Figure 4.
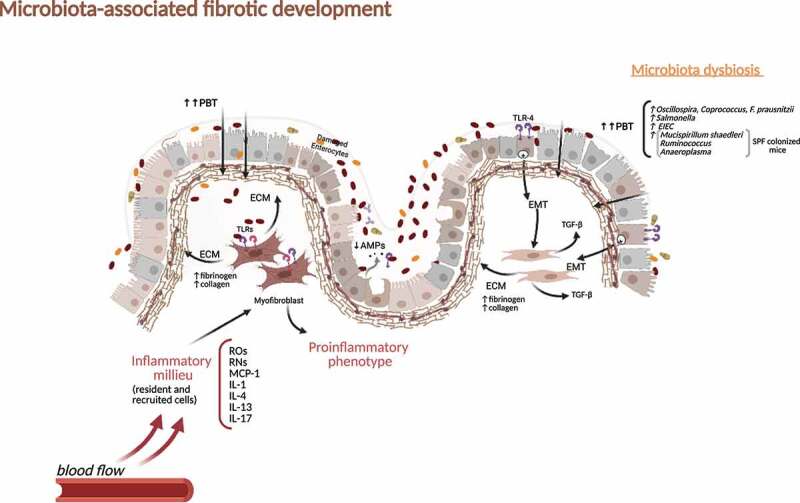
Intestinal fibrosis development during microbiota dysbiosis in Crohn’s disease. Mediators generated during sustained inflammation and continued PBT favored by gut barrier distortion induce myofibroblasts activation and extracellular matrix production with deposition of fibrinogen and collagen. Intestinal epithelial cells undergo EMT after activation of TLR-4 and contribute to the fibrotic context by inducing TGF-β. PBT, pathological bacterial translocation; TLRs, Toll-like receptors; ECM, extracellular matrix; EMT, epithelial to mesenchymal transition; ROs, reactive oxygen species; RNs, reactive nitrogen species; MCP-1, Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1; IL, interleukin; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-beta; SPF, Specific-pathogen-free; EIEC, Enteroinvasive Escherichia coli.
