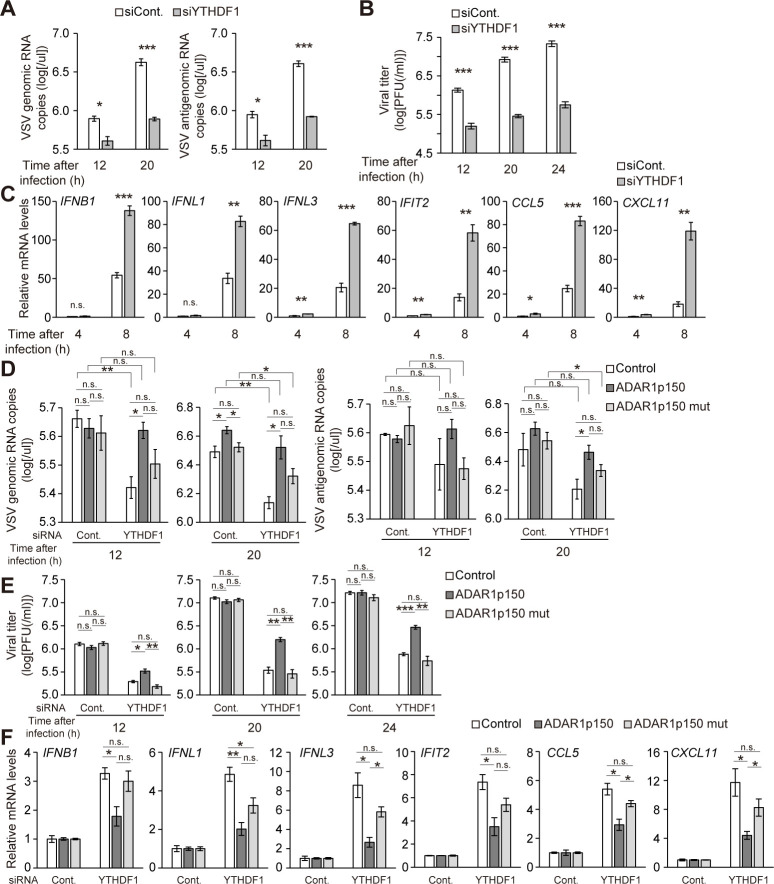
Fig 5. YTHDF1 knockdown inhibits viral replication in cells.
(A) RT-qPCR showing significant decrease in the expression of VSV genome RNA and antigenome RNA upon YTHDF1 knockdown at 12 and 20 h after rVSV-GFP infection. (B) Viral titers in culture medium at 12, 20, and 24 h after rVSV-GFP infection were determined by plaque assay. YTHDF1 knockdown inhibited the release of infectious virus. (C) RT-qPCR showing elevated expression levels of IFN genes, ISGs, and NF-κB–inducible genes upon YTHDF1 knockdown at 4 and 8 h after rVSV-GFP infection. The signals were normalized to GAPDH. (D) RT-qPCR showing knockdown effect of YTHDF1 on the expression of VSV genome RNA and antigenome RNA at 12 and 20 h after rVSV-GFP infection in stable cell lines. (E) Viral titers in culture medium at 12, 20, and 24 h after rVSV-GFP infection were determined by plaque assay. (F) RT-qPCR showing knockdown effect of YTHDF1 on IFN genes, ISGs, and NF-κB–inducible genes in stable cell lines. The signals were normalized to GAPDH and then normalized to control siRNA samples. (A–F) Two-tailed Student t tests were performed to assess the statistical significance of differences between groups, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, n.s. p ≧ 0.05. n = 3 for all experiments. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. The numerical values for this figure are available in S1 Data. IFN, interferon; ISG, IFN-stimulated gene; n.s., not significant; RT-qPCR, quantitative reverse transcription PCR; rVSV-GFP, recombinant GFP-expressing vesicular stomatitis virus; SEM, standard error of the mean; siRNA, small interfering RNA.