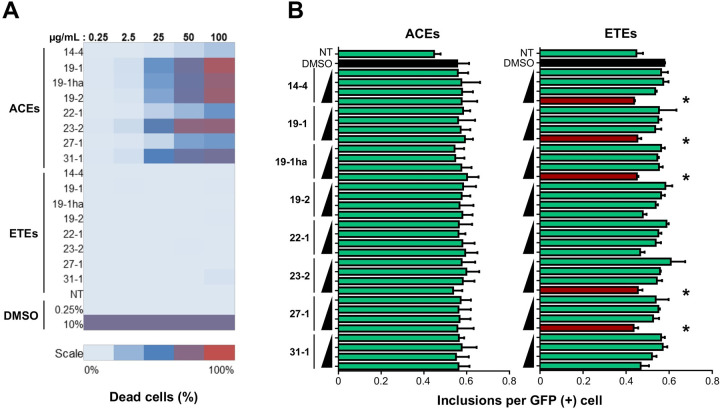
Fig 2. Treatment with extracts from different genotypes of U. molinae fruits exerts differential effects on cell viability and the number of polyQ79-EGFP inclusions in HEK293 cells.
The analysis was performed in the cellomics platform of automated fluorescence microscopy. (A) For the cell viability analysis, cells were seeded and then treated with increasing concentrations of each extract. After 24 h, cells were treated with 7-AAD and images were acquired with the cellomics platform. 7-AAD-stained cells were quantified using the General intensity measurement tool. Data was acquired using the HCS Studio® software. (B) For the analysis of the effects over polyQ79-EGFP inclusions, cells were transfected and then treated with increasing concentrations of each extract. A range of concentrations from 3.1 to 12.5 µg/mL were analyzed for ACEs, except for ACE 14–4 (12.5 to 100 µg/mL). For ETEs, concentrations from 12.5 to 100 µg/mL were analyzed. After 24 h, images were acquired in the cellomics platform and GFP (+) protein inclusions were quantified using the spot detector application. Data was acquired using the HCS Studio® software. Results are the mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. Statistically significant differences were detected by one-way ANOVA and Tukeys multiple comparisons considering DMSO as control (* = p < 0.05).