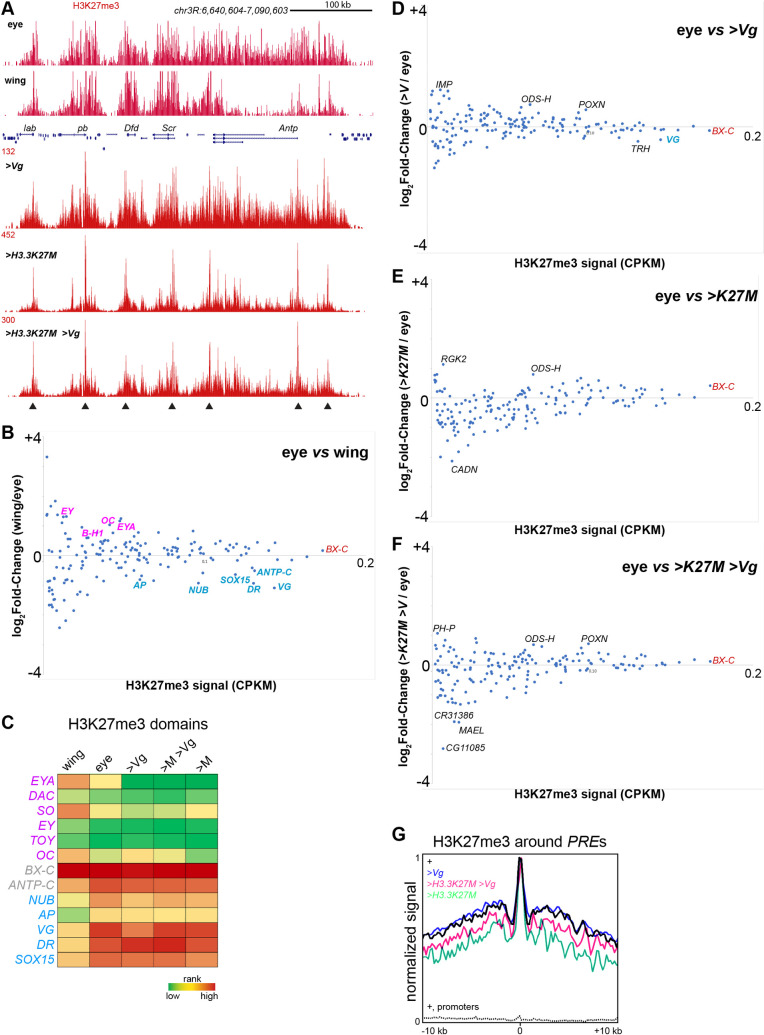
Fig 5. Chromatin profiling of H3K27me3 domains in reprogrammed eye imaginal discs.
(A) Chromatin profiling at the ANTP-C H3K27me3 domain in wing and eye imaginal discs. Arrowheads mark the positions of major Polycomb-bound PREs. (B) Changes in average fragment density (CPKM) of H3K27me3 in 166 annotated Polycomb domains between wing and eye imaginal discs. Domains are ranked by decreasing average H3K27me3 CPKM in wing and eye imaginal discs. Selected domains containing eye-specific genes (pink), wing-specific genes (blue) or common repressed genes (red) are marked. (C) Selected domains including eye-specific genes (pink), wing-specific genes (blue) or common domains (grey) are shown for wing and eye controls and production of Vg and H3.3K27M. (D-F) Changes in average fragment density (CPKM) of H3K27me3 in Polycomb domains between w1118 eye imaginal discs and discs with H3.3K27M and Vg production. Selected domains with the largest changes in chromatin methylation are marked. (G) Average H3K27me3 coverage around 700 Polycomb-bound PREs [24] within H3K27me3 domains (solid lines), and around promoters (dashed line).